| Module | Name | Version | License | Source | Languages | Platforms | Type | Author | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP | HTTP-realization | 3.1 | GPL2 | prot_HTTP.so | en,uk,ru,de | x86,x86_64,ARM | Protocol | Roman Savochenko Maxim Lysenko (2009) — the page translation |
Provides support for the HTTP protocol for WWW-based user interfaces. |
Contents
Module of the transport protocol HTTP is designed to support the implementation of the network protocol HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) in OpenSCADA.
HTTP protocol is used to transfer the WWW content. For example, via HTTP the following types of documents are transmitted: html, xhtml, png, javascript, and many others. Support HTTP in OpenSCADA together with the transport Sockets allows to implement various user functions based on the WWW interface. The module implements two main methods of the HTTP protocol: "GET" and "POST". The module provides control of the integrity of HTTP-queries and, jointly with "Sockets" transport, allows to "collect" whole requests from their fragments, as well as hold of the connection "alive" (Keep-Alive).
For flexible connection of the user interfaces to this module, the modular mechanism within the module itself is used. In the role of modules the modules of the subsystem "User interfaces" are used with the additional information field "SubType", with the value of "WWW".
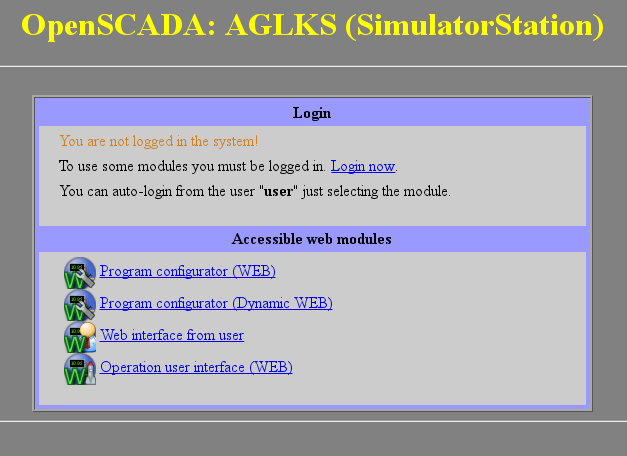
In the requests for the Web resources the URL(Universal Resource Locator) are commonly used. Hence, the URL is passed as the main parameter via HTTP. The first element of the requested URL is used to identify the module UI. For example, the URL "http://localhost:10002/WebCfg" means requesting to the module "WebCfg" on the host "http://localhost:10002". In the case of an incorrect indication of the module ID, or when you address without identifier of the module at all, the module generates the information dialogue on the entry and the choice of one of the available user interfaces. Example of the dialogue is shown in Figure 1.
The module supports multi-language which one enabled by the dynamic messages translation of OpenSCADA.
The language of the final user interface is determined by and in sequence:
- URL's parameter "lang".
- Authenticated user's language.
- Language of the Web-browser from the HTTP property "Accept-Language".
- Generic language of the OpenSCADA process.
Gotten in the way language used for building interfaces of the module and passes to the WWW sub-modules into the HTTP property "oscd_lang" of the argument "vars" of the "GET" and "POST" functions.
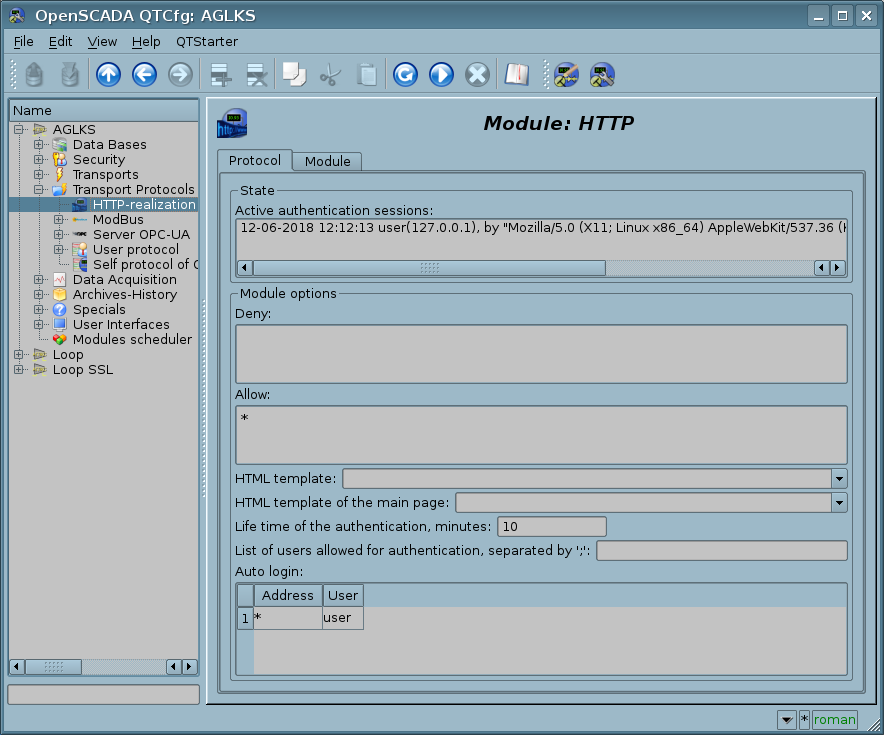
To configure and control this module, you will have the configuration page of the OpenSCADA control interface (Fig. 3) where you can perform:
- Control for the active authentication sessions.
- Configuring:
- Rules of accessing for deny and allow. Any line of the rules of accessing is a different rule and you can use here templates, like to "*/WebVision/*"), or regular expressions, like to "/[^/]+/WebVision/.+/".
- HTML-template of the user interface and user main-page. In the HTML-template's fields you must specify an address of the file HTML/XHTML, which will be used for formation of the internal-service and main-page interfaces. Internal-service interfaces for example, it's the WEB-modules selection, the login page and like ones of the WEB-modules. From the template required correct XHTML, allowing parse the file by XML-parser, and the presence of the tag "#####CONTEXT#####" at the location of the dynamic content, for internal-service interfaces it's necessarily. Resource files of the templates represented by images, CSS and JavaScript files and their are searching from the directory in which located the specified template file and from the current directory. If errors are found in the template there will be use a standard builtin interface. For different, to the language, template file you can add the language suffix to the file end like "{My template}_{lang}.html" but select the generic-base template file "{My template}.html" into these configuration fields. For the templates example you can see to the most used templates:
- Internal-service and main-page interfaces template, includes the modules index.
- Main-page's template with a direct link to the AGLKS main interface by UI.WebVision and without the WEB-modules index.
- Main-page's template with a strong redirection to the AGLKS main interface by UI.WebVision.
- The lifetime of the authentication, list of the users allowed for authentication and set up of the automatic login.
1 Authentication
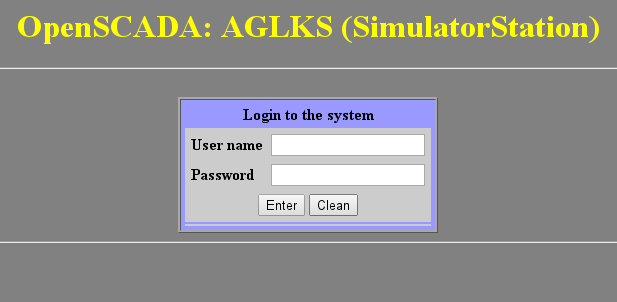
The module supports authentication in OpenSCADA while providing access to the WEB-interface modules (Fig.2).
To facilitate with Web-based interfaces, the module provides for automatic login from the specified user's name. Configuring for the automatic login makes by the module settings page (Fig.3). Automatic login performs by matching the address indicated in the column "Address", and on behalf of the user specified in the column "User".
For greater security, you can only identify Web users in the list of users allowed to authenticate.
2 Modules of the WEB-interface
Modules of the user interface (UI) designed to work with HTTP module, should indicate the information field "SubType" with the value "WWW" and "Auth" field with the value "1", if the module requires an authentication at login. For communication of HTTP module and UI modules an advanced communication mechanism is used. This mechanism involves the export of interface functions. In this case, the UI modules must export the following function:
- void HTTP_GET(const string &url, string &page, vector<string> &vars, const string &user, TProtocolIn *iprt); OR
- void HttpGet( const string &url, string &page, const string &sender, vector<string> &vars, const string &user ); — GET method with the parameters:
- url — address of the request;
- page — page with the answer;
- sender — address of the sender;
- vars — variables of the request;
- user — user;
- iprt — pointer to an input part object of the protocol.
- void HTTP_POST(const string &url, string &page, vector<string> &vars, const string &user, TProtocolIn *iprt); OR
- void HttpPost( const string &url, string &page, const string &sender, vector<string> &vars, const string &user ); — POST method with the parameters:
- url — address of the request;
- page — page with the answer and with the content of the body of the POST request;
- sender — address of the sender;
- vars — variables of the request;
- user — user;
- iprt — pointer to an input part object of the protocol.
Then, in the case of the HTTP "GET" request, the function "HTTP_GET" or "HttpGet" will be called, and in the case of the "POST" request, the function "HTTP_POST" or "HttpPost" will be called in the appropriate UI module.
3 Function of the output requests of the user API
The output request function (messIO()) operates the exchange of contents of HTTP requests wrapped in XML packets. The query structure has the form:
<req Host="host" URI="uri">
<prm id="pId">pVal</prm>
<cnt name="cName" filename="cFileName">
<prm id="cpId">cpVal</prm>
cVal
</cnt>
reqVal
</req>
- Where:
- req — request method, supported methods "GET" and "POST".
- host — http-server address in the format {HostAddr}:{HostIp}. If this field is omitted, then the host address specified in the transport address field is used.
- uri — resource address at the http server, file or directory.
- pId, pVal — identifier and value of addition http-parameters. You can set multiply http-parameters setting different prm tags.
- cName, cFileName, cVal — name, file-name and value of the content-element of the POST-request. You can set multiply content-elements setting different cnt tags.
- cpId, cpVal — identifier and value of addition content-parameters. You can set multiply content-parameters setting different prm tags;
- reqVal — single content of the POST request.
The query result is the response structure:
<req Host="host" URI="uri" err="err" Protocol="prt" RezCod="rCod" RezStr="rStr"> <prm id="pId">pVal</prm> respVal </req>
- Where:
- req — request method.
- host — http-server address.
- uri — resource address.
- err — error occurring during the request. In the case of a successful request, this field is empty.
- RezCod, RezStr — query result in the form of code and text.
- pId, pVal — identifier and value of the addition http-parameter. Http-parameters can be many, defined by the individual prm tags.
- respVal — content of the response.
Here is the formation of GET and POST requests in the JavaLikeCalc.JavaScript language, as an example of using this function in user procedures:
//GET request for a HTML-page
req = SYS.XMLNode("GET");
req.setAttr("URI","/");
SYS.Transport.Sockets.out_testHTTP.messIO(req,"HTTP");
test = req.text();
//GET request and saving a file
req = SYS.XMLNode("GET");
req.setAttr("URI","/oscadaArch/Work/openscada-0.9-r2188.tar.lzma");
SYS.Transport.Sockets.out_testHTTP.messIO(req,"HTTP");
if(!req.attr("err").length) SYS.fileWrite("/var/tmp/recvFile.tmp", req.text());
//POST request
req = SYS.XMLNode("POST");
req.setAttr("URI","/WebUser/FlowTec.txt");
cntNode = req.childAdd("cnt").setAttr("name","pole0").setAttr("filename","Object2-k001-100309-17.txt");
cntNode.childAdd("prm").setAttr("id","Content-Type").setText("text/plain");
cntText = "Object2-k001\r\n";
cntText += "\r\n";
cntText += "v002\r\n";
cntText += " n1\r\n";
cntText += " 09.03.10 16 Polnyj 7155.25 216.0 32.000 17.5\r\n";
cntText += "v005\r\n";
cntText += " n1\r\n";
cntText += " 09.03.10 16 Polnyj 188.81 350.0 4.000 40.0\r\n";
cntText += "\r\n";
cntNode.setText(cntText);
SYS.Transport.Sockets.out_testHTTP.messIO(req,"HTTP");
4 User programming API
The module object (SYS.Protocol.HTTP)
- bool pgAccess(string URL) — checks for accessing the page, pointed by the URL.
- URL — URL of the checking page.
- string pgCreator(string cnt, string rcode = "200 OK", string httpattrs = "Content-Type: text/html;charset={SYS}", string htmlHeadEls = "", string forceTmplFile = "", string lang = "" ) — forms for a page or a resource from the content cnt, wrapped to HTTP with the result rcode, with HTTP additional attributes httpattrs, HTML additional head's element htmlHeadEls, forced to template file forceTmplFile and language lang.
- cnt — content of the page or the resource (images, XML, CSS, JavaScript, ...) ;
- rcode — HTTP result code, like to "200 OK"; empty value there disables addition of the HTTP header;
- httpattrs — additional HTTP-attributes, mostly this is "Content-Type" which by default sets to "text/html;charset={SYS}"; only for "Content-Type: text/html" will be wrapped to internal/service or force forceTmplFile HTML-template;
- htmlHeadEls — additional HTML-header's tag, it's mostly META with "Refresh" to the specified URL;
- forceTmplFile — force template file to override the internal/service or the main-page template.
- lang — language of the forming interface.