| Module | Name | Version | License | Source | Languages | Platforms | Type | Author | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTStarter | Qt GUI starter | 4.5 | GPL2 | ui_QTStarter.so | en,uk,ru,de | x86,x86_64,ARM | UI | Roman Savochenko Maxim Lysenko (2009) — the page translation |
Provides the Qt GUI starter. Qt-starter is the only and compulsory component for all GUI modules based on the Qt library. |
Contents
The module provides OpenSCADA with the starter of the GUI modules on the multi-platform library Qt of the graphical user interface (GUI) of initially created by the firm TrollTech. Also, the module implements elements of the OpenSCADA project manager. A separate module of running the Qt GUI modules and elements of the OpenSCADA project manager is needed because of the need for single-flow execution of all visual components of Qt and centralized initialization of the main object of the Qt-library — QApplication.
From the beginning, this module creates a separate thread for the main Qt thread, where it is possible to create a dynamic splash screen (Fig.1), since the main OpenSCADA processes continue to run in the main thread. That version of Qt5 was sensitive to execution in a non-main thread, so for OpenSCADA it was added to this feature, but only with a static splash screen. To control this feature, the OpenSCADA build configuration parameter --enable-QtMainThrd is provided, which by default is disabled for Qt4 and enabled for Qt5.
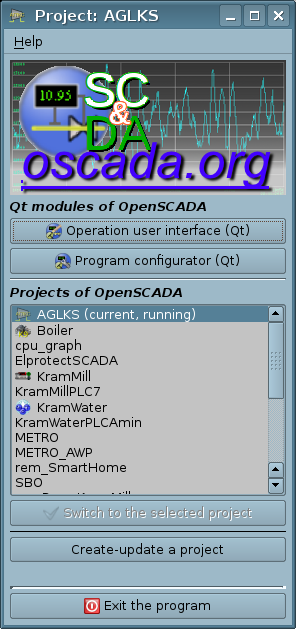
The starter dialog window (Fig.2) in whole provides:
- a choice of the available Qt GUI modules, may not be available in the case of initial launch to select only the OpenSCADA project;
- a choice of the available OpenSCADA projects to their selection or switching;
- exiting of OpenSCADA;
- the help menu with items: "About", "About Qt", "QTStarter manual" (F1), "OpenSCADA 0.9 manual" and "What's This" (Shift+F1).
In the case of missing the starter dialog window and all windows of the Qt GUI modules, the program can be started up or collapsed to the system tray (Fig.3) created by this module.
The module disables the function of saving the program session when the system is shut down, in order to prevent attempts to restore this session at the system startup, since OpenSCADA does not need it.
1 Qt modules of OpenSCADA
To run Qt GUI modules, an advanced interface for calling module functions is used. This interface involves exporting of functions by the external modules. In our case, Qt GUI modules must export the following functions:
- QIcon icon(); — sends an object of icon of the called module, for the list building.
- QMainWindow *openWindow(); — creates an object of the main window of the Qt GUI module, and passes it to the starter. It can return NULL in the case of the failure to create a new window.
For the identification, a Qt GUI module must define the information item "SubType" of the module as "Qt". Proceeding from this sign, "Starter" works with it.
After receiving the object of the main window, "Starter" simply displays it, and the module window can additionally add the "Starter" elements, in the form of a general list of Qt modules of OpenSCADA, to call them from this window. The general list of Qt modules of OpenSCADA can be added to the menu or toolbar of the window by calling the "makeStarterMenu(QWidget *mn = NULL)" slot of the QApplication class from "Starter", where mn indicates a widget of the QAction container or the main window menu for NULL.
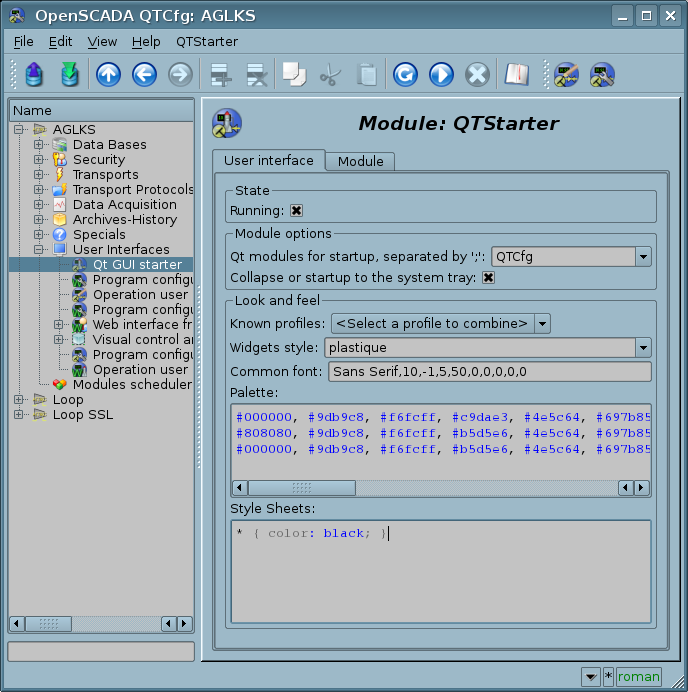
To specify Qt GUI modules that start at startup, the starter module contains the "StartMod" configuration field. This field specifies the identifiers of the modules that are started. The "StartMod" configuration field can be defined in the configuration file as well as in the system table of the database ("SYS") via a dialog of the module configuration (Fig.4).
In the case of closing the windows of all Qt GUI modules or starting without defining the module to start in the "StartMod" field, "Starter" creates its own dialog (Fig.2). If the "CloseToTray" field of the configuration file or module configuration (Fig.4) is installed then in this case, the program will be collapsed to the system tray (Fig.3).
2 OpenSCADA projects
With the integration into OpenSCADA elements of the project manager, this module received the function of selecting existing and creating new OpenSCADA projects in the list of the projects and project commands (Fig.2). Currently, there are two modes of the starter dialog window (Fig.2), which is the mode of the initial start and the mode of execution of the selected project.
The initial mode is, in fact, a launch mode without a specific project, and it involves choosing a project for switching to the second mode, and accordingly hides the list of Qt GUI modules, even if they are loaded to the initiating configuration.
In the project execution mode, all common mechanisms work, that is a call to Qt GUI modules and a start-collapse in the system tray, and the startup dialog (Fig.2) contains a list of available Qt GUI modules and the information about the running project in the title of the window.
In addition to the names of the projects in the list of projects, to the right of the title, their status is "current" and "running". The state of "current" means that the execution of this particular project is carried out. The state "running" indicates a multiple-start blocking file presence, and thus the execution of the project, and separately from this project if the state "current" is not specified next. You can select and try to switch to a project in the "executable" state by accepting the warning, but if this project is actually executed now and the presence of the lock file is not residual after the program crash, then the switching program just ends!
3 Look and feel
Due to the expansion of the use of OpenSCADA to mobile software platforms such as Maemo, MeeGo, Android, and frequent cases of QT4 and Qt5 libraries mismatches to modern desktop environments, this module has been expanded by its own mechanism for controlling the look and feels of the final visual interface.
In general, the module now controls overall: Qt widget style, common font, interface palette, and cascading style sheets. This control is performed through the parameters of the configuration file "Style", "Font", "Palette", "StyleSheets" and module configuration (Fig.4).
Also, the module provides fixing of the outcomes of the individual looks and feelings in a library of the composite nature, which is formed in a configuration file table with the structure: LookFeel(NAME, STYLE, FONT, PALETTE, STL_SHTS).
Therefore, for mobile devices or predefined specific desktop environments, the required look and feel can be pre-installed in the program package configuration file, but for everyone you can quickly change it after installation by selecting the one you want from the library.
4 Configuration
To configure the functions shown above, the module provides the ability to configure their parameters through the OpenSCADA control interface (Fig. 4):
- Section "Module options":
- Qt modules for startup, separated by ';'.
- Collapse or startup to the system tray.
- Section "Look and feels", changes are not applied immediately and require overload:
- Known profiles — a combobox with a list of profiles in the library and a series of commands over the current profile:
- "<Clear>" — clear the current profile;
- "<Read back>" — read back the profile from the current Qt settings, only in the cleaned profile items.
- "{Profile name}" — read the value from the specified profile name and add-combine with the current one if it is not empty.
- Widgets style — the profile field allows you to select from the list known styles in this configuration Qt and is not composite.
- Common font — the Qt common font which specifies icons size also.
- Palette — the field of the color profile of the interface in three groups of rows: active, disabled, inactive. But with twenty colors in the group line, separated by the character ',': WindowText(0), Button(1), Light(2), Midlight(3), Dark(4), Mid(5), Text(6), BrightText(7), ButtonText(8), Base(9), Window(10), Shadow(11), Highlight(12), HighlightedText(13), Link(14), LinkVisited(15), AlternateBase(16), NoRole(17), ToolTipBase(18), ToolTipText(19). The profile allows you to define only the colors you want, leaving the indeterminate as the empty ones, which determines the composite palette, that is filling the voids with another library profile.
- Style Sheets — the field of Cascading Style Sheets Profile (CSS), the composite of which is to add CCS rules at the end of the current profile.
- Known profiles — a combobox with a list of profiles in the library and a series of commands over the current profile:
5 User programming API
The module object (SYS.UI.QTStarter)
- Array sensors() — get all available sensors of the Qt mobility, returns "false" if no sensor is available.