| Module | Name | Version | License | Source | Languages | Platforms | Type | Author | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCAEngine | Visual control area engine | 5.1 | GPL2 | ui_VCAEngine.so | en,uk,ru,de | x86,x86_64,ARM | UI | Roman Savochenko Maxim Lysenko (2011-2012) — the page translation |
The main engine of the visual control area. |
Contents
- 1 Purpose
- 2 Configuration and formation of the VCA interfaces
- 3 Architecture
- 3.1 Frames and elements of the visualization (widgets)
- 3.2 Project
- 3.3 Session of the project execution
- 3.4 Styles
- 3.5 Events, their processing and the events' maps
- 3.6 Signaling (Alarms)
- 3.7 Rights management
- 3.8 Linkage with the dynamics
- 3.9 Primitives of the widgets
- 3.9.1 Elementary graphical figure (ElFigure)
- 3.9.2 Element of the form (FormEl)
- 3.9.3 Text element (Text)
- 3.9.4 Element of visualization of media-materials (Media)
- 3.9.5 Element of constructing diagrams (Diagram)
- 3.9.6 Element of building the protocols based on the message archives (Protocol)
- 3.9.7 Element of formation of the documentation (Document)
- 3.9.8 Container (Box)
- 3.10 Database using to store libraries of widgets and projects
- 3.11 API of the user programming and service interfaces of OpenSCADA
- 3.11.1 API of the user programming
- 3.11.2 Service interfaces of OpenSCADA
- 3.11.2.1 Access to the attributes values of the visualization elements (widgets)
- 3.11.2.2 Group access to the values of the attributes of the visualization elements (widgets)
- 3.11.2.3 Access to the session pages
- 3.11.2.4 Control for signaling (alarming)
- 3.11.2.5 Manipulation with the sessions of the projects
- 3.11.2.6 Group request for the tree of the widgets libraries
- 4 Configuring the module via the control interface of OpenSCADA
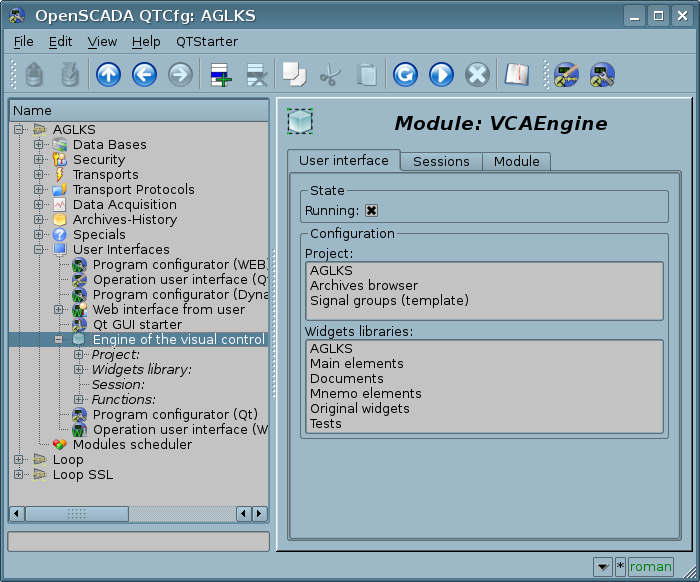
The module provides OpenSCADA for visual control area engine (VCA). The module itself does not implement visualization of VCA, but contains data in accordance with the concept "Model/Data — Interface". The visualization of this module's data is performed by the visualization modules of VCA, such as Vision and WebVision.
Visual control area (VCA) is an integral part of the SCADA system. It applies to the client stations with a view to providing accessible information about the control object and to for the the issuance of the control actions to the object. In various practical situations and conditions the VCA, based on different principles of visualization, may by applied. For example, this may be the library of widgets Qt, GTK+, WxWidgets or hypertext mechanisms based on the technologies HTML, XHTML, XML, CSS and JavaScript, or third-party applications of visualization, realized in various programming languages Java, Python, etc. Any of these principles has its advantages and disadvantages, the combination of which could become an insurmountable obstacle to the use of VCA in a practical case. For example, technologies like the Qt library can create highly-productive VCA, which will undoubtedly important for the operator station for control the technological processes (TP). However, the need for installation of that client software in some cases may make using of it impossible. On the other hand, Web-technology does not require installation on client systems and is extremely multi-platform (it is enough to create a link to the Web-server at any Web-browser) that is most important for various engineering and administrative stations, but the productivity and reliability of such interfaces is lower, that actually eliminates the using of them at the operator stations of TP.
OpenSCADA has extremely flexible architecture that allows you to create external interfaces, including user, in any manner and taste. For example, the OpenSCADA configuration environment available now as by means of the Qt-library, and also the Web-based.
At the same time, independent creation of the VCA implementations in different basis may cause the inability to use the configuration of one VCA into another one. That is inconvenient and limited from the user side, as well as costly in terms of implementation and follow-up support.
In order to avoid these problems, as well as to create as soon as possible the full spectrum of different types of VCA, the project for the construction of the concept of VCA is founded. The result of this project was this engine module (data model) of VCA, as well as direct visualization modules Vision and WebVision.
1 Purpose
This engine module (data model) of the VCA is aimed to create the logical structure of the VCA and the execution of sessions of individual instances of the VCA projects. Also, the module provides all the necessary data to the final visualizers of the VCA, both through local mechanisms of interaction of OpenSCADA, and through the control interface of OpenSCADA for remote access.
Final version of the VCA module will provide:
- three levels of difficulty in the formation of the visualization interface, which allow organically to develop and apply the tools by the principle — from simple to complex:
- formation from the template frames, by assigning the dynamics and without the graphical configuration;
- graphical formation of new frames, using ready-made visualization elements from the library - mnemosmes;
- forming, in the library, new ones: frames, template frames and display elements.
- construction of interfaces for visualization of practically any complexity (limited by the "discreteness" of the primitive functions), ranging from simple monitoring interfaces, and to complete hierarchical interfaces used in SCADA systems;
- providing the different ways of forming and configuration of the user interface, based on different interfaces of graphical representation (Qt, Web, ...), or-through the standard interface of OpenSCADA control;
- construction and correction of the interface, appointment and change of the dynamics in the process of the execution;
- construction, at the user level, of new template frames and the formation of specialized ones, under the scope, libraries of frames (e.g. the inclusion of parameters frames, diagrams and other elements linking them to each other), according to the idea of secondary use, accumulation and improvement;
- construction of new custom visualization elements and the formation of specialized, at the field of application, libraries of frames, according to the idea of secondary use, accumulation and improvement;
- description of the logic of new template frames and user visualization elements as by the simple links as well by the compact and full-featured user programming language;
- possibility of inclusion, to the user's visualization elements, the functions (or frames of functions' calculation) of the object model of OpenSCADA, practically linking the presentation with the algorithm of computation, for example, visualizing the library of the apparatus of TP models for subsequent visual building of the TP models;
- separation the data of the user interfaces and presentation interfaces of these data, allowing to build the user interface in the one environment, and execute in many others (Qt, Web, ...);
- ability to connect to the executable interface for monitoring and correction of actions; for example, training operators and monitoring their actions in real time;
- visual construction of various schemes with overlapping logical connections and subsequent centralized execution in the background - visual construction and execution of mathematical models, logic circuits, relay circuits and other;
- providing, to OpenSCADA, object API functions; can be used to control the properties of the visualization interface from user procedures;
- server construction for: frames, visualization elements and visualization interface projects; with the ability to service multiple client connections;
- simple organization of client stations on different bases (Qt, Web, ...) with the connection to the central server;
- full-featured mechanism for distributing authorities between users that allows you to create and execute projects with different rights to access their components;
- flexible formation of rules of alarms and notifications, with the support of various methods of the notification;
- support of custom formation of the palette and font preferences for the visualization interface, in styles;
- support of the user forming of the events maps under various control equipment and user's preferences;
- support for user profiles, allowing the identification of various properties of the visualization interface (colors, font features, the preferred card of events);
- flexible storage and distribution of libraries of widgets, frames and projects of the visualization interfaces in the databases, supported by OpenSCADA; practically, the user only has to register the received database with the data.
2 Configuration and formation of the VCA interfaces
Module itself does not contain mechanisms for visual creating interfaces of VCA, such tools can be given by the final visualization modules of the VCA, for example such a tool provides by the module Vision.
Although the mechanisms for the visual formation of the VCA the module doesn't provide, the interface to manage the logical structure is provided, implemented on the basis of the control interface of OpenSCADA, and thus it is available for use in any OpenSCADA configurator. Dialogues of this interface are considered further in the context of the architecture of the module and its data.
3 Architecture
VCA, in whole, can operate in two modes — the development and running. In the mode of development, the interface of the VCA and its components is formed, the mechanisms of interaction are determined. In the execution mode, performes the formation of the UI interface and the interaction with the end user, based on the developed VCA.
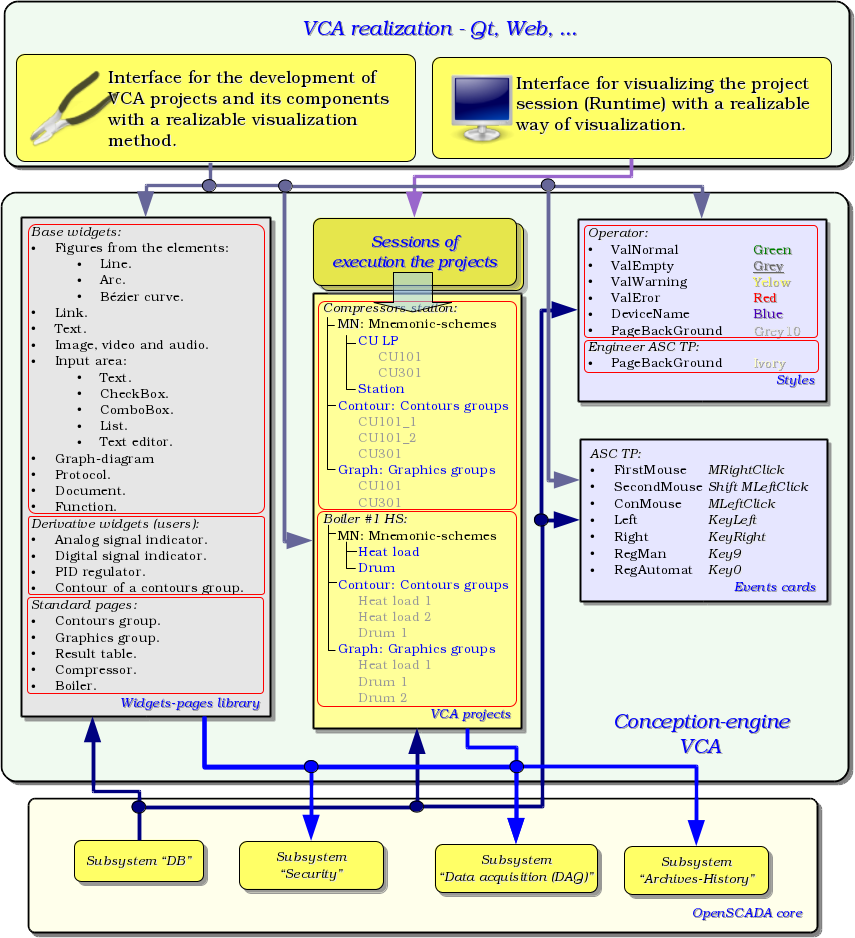
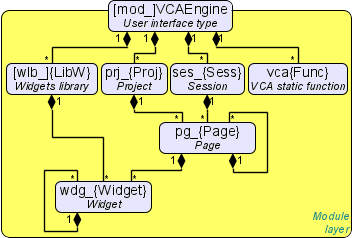
VCA interface is formed of the frames, each of which, in its turn, formed from elements of the primitives, or user interface elements. Herewith, the user interface elements are also formed from the primitives or other user elements. That gives us a hierarchy and reuse of already developed components.
Frames and user elements are placed in the libraries of widgets. The projects of the interfaces of the final visualization of the VCA are formed from these libraries' elements. Based on these projects the visualization sessions are formed.
The described VCA structure is shown in the Figure.
That architecture of the VCA allows the support of three levels of complexity of the developing process of the control interface:
- Forming of the visualization and control (VC) interface using the library of template frames by placing the templates of the frames in the project and by the assignment of the dynamics.
- In addition to the first level, performing of the formation of own frames based on the library of derivatives and basic widgets. Perhaps as a direct appointment of the dynamics in the widget, and the subsequent appointment of it in the project.
- In addition to the second level, performing of the independently forming of derivatives widgets, new template frames and also the frames with the use of mechanism of describing the logic of interaction and handling of events in the user programming language of OpenSCADA.
3.1 Frames and elements of the visualization (widgets)
Frame is the window, which directly provides information to the user in graphical or text form. The group of interconnected frames creates whole user interface of VC.
Content of the frame forms from the visualization elements (widgets). Widgets may be the basic primitives (different elementary figures, text, trend, etc.) and derivative, formed from the basic or other derivative widgets. All widgets are grouped by libraries. In the process of the work, the user can create his own libraries of derivative widgets.
Actually the frame itself is also a widget that is used as a final element of visualization. This means that the widget libraries can store the blanks of frames and the templates of the resulting pages of the user interface.
Frames and widgets are passive elements that do not normally contain links to the dynamics and other frames, but only provide information about the properties and the nature of the dynamics (configuration), connected to the properties. Activated frames, i.e. containing links to the dynamics and active connections, form the user interface and are stored in the projects. In some cases, it is possible the direct appointment of the dynamics in the blanks of frames.
Derivative frames/widgets can contain included widgets, which can be glued-linked of one another with the logic by the user programming language of OpenSCADA.
The widget is an element through which the following is provided:
- visualization of operational and archive information about TP;
- alarming about violations of conduction the TP;
- switching between the frames of TP;
- control of the technological equipment and the parameters of conduction the TP.
Setting and linkage of the widgets is done through their properties. Parent widget and the widgets it contains, can be complemented by user properties. Then, the user and static attributes, are associated with the properties of included widgets by internal logic. To show the dynamics (current and archived data), properties of the widgets are dynamized, that is linked with the attributes of the parameters of OpenSCADA or properties of other widgets. Using, for linking nested widgets by internal logic, the user programming language of OpenSCADA relieves the issue of implementing a complex visualization logic, thus providing high flexibility. Practically, you can create fully dynamized frames with complex interactions at the user level.
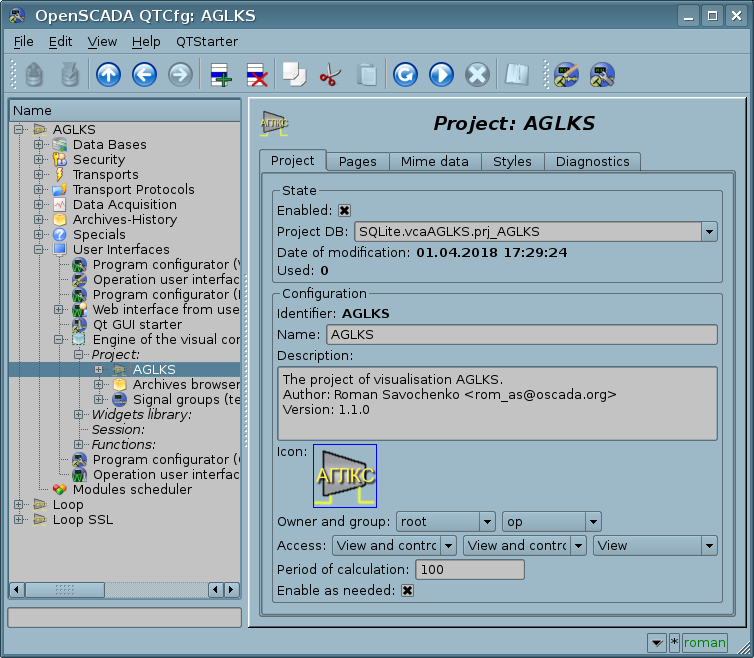
3.2 Project
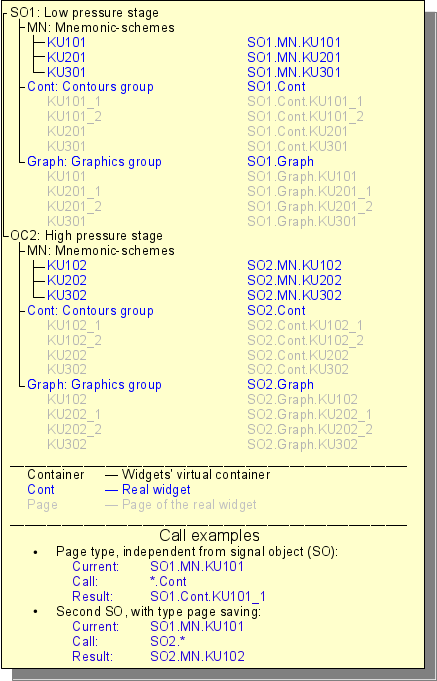
The direct configuration, and the properties of the final visualization interface, are contained in the visualization interface project of VCA, which can be created a lot.
Each project includes pages from the libraries of the frames/widgets. For a number of modes, the page itself may include nested pages as parent-independent and using parent as a template. The template pages-widgets allow to extremely simplify the process of creating the same type of the frames for easy monitoring by the ACS-TP engineer or the user OpenSCADA. An example of such one-type frames may be: groups of contours, groups of graphs, reports and various summary tables. Mnemonic schemes of the technological processes rarely fall under such scheme and are formed on a separate page-widget.
The page, like the widget on which it is based, provides the ability to bind the dynamics to the properties described in it — links that can be set by dynamics or constants. In addition, linking directly at the project page level are more preferable than performing it at the library widget level.
Example of hierarchical representations of components of the project of the classical interface of VC of the technological process with the description of standard call expressions is given in Figure.
The following special page properties are provided:
- Container — page is the container for the underlying pages.
- Template — page is the template for the underlying pages.
- Empty — empty and inactive page. This property is used in conjunction with the property Container for organization the logical containers.
Based on combinations of these properties the following types of pages are realized:
- Standard — the standard page (no property), it is the full-featured final page.
- Container — the full-featured page with the property of the container (Container).
- Logical container — the logical container is actually not a page (Container|Empty), acts as an intermediate and group element in the page tree.
- Template — the template page (Template). Pure template page that is used to describe common properties and to identify them in nested pages, privately.
- Container and template — the template and container page (Template|Container), combines the functions of the template and the container.
On the visualization side (RunTime) a logic is constructed that governs how to open pages based on the following attributes of the basic element "Box":
- pgOpen — sign "The page is opened";
- pgNoOpenProc — sign "Execute the page, even if it is not opened";
- pgOpenSrc — contains the widget address or the page that opened the current page; in the case of an included container widget, here is the address of the included page; to open a page from a script it is enough to specify the address of the widget-source of opening;
- pgGrp — group of pages used to link container pages to pages, according to a common group.
The logic of determining how to open pages works like this:
- if the page has the group "main" or coincides with the page group in the main window or there is no page on the main window, then open the page in the main window;
- if the page has a group which coincides with the group one of the containers of the current page, then open it in the container;
- if the source of the opening page coincides with the current page, then open it as an additional window over the current page;
- send the call to the opening request for additional windows, processing each of the first three items;
- if any one of the relative windows doesn't open the new page, then open it as a related window of the main window.
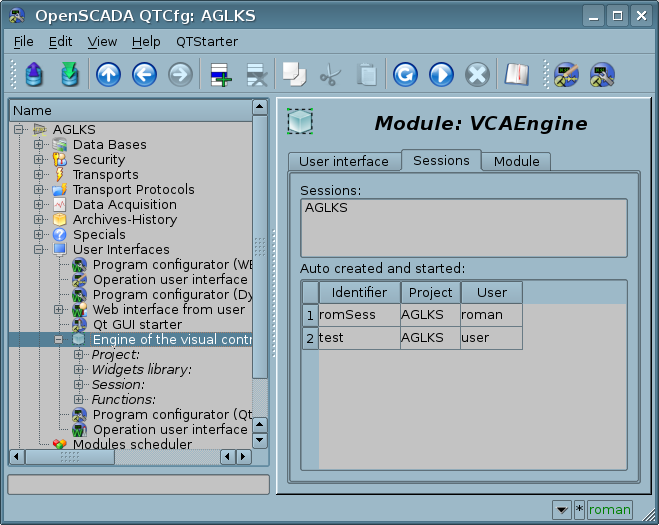
3.3 Session of the project execution
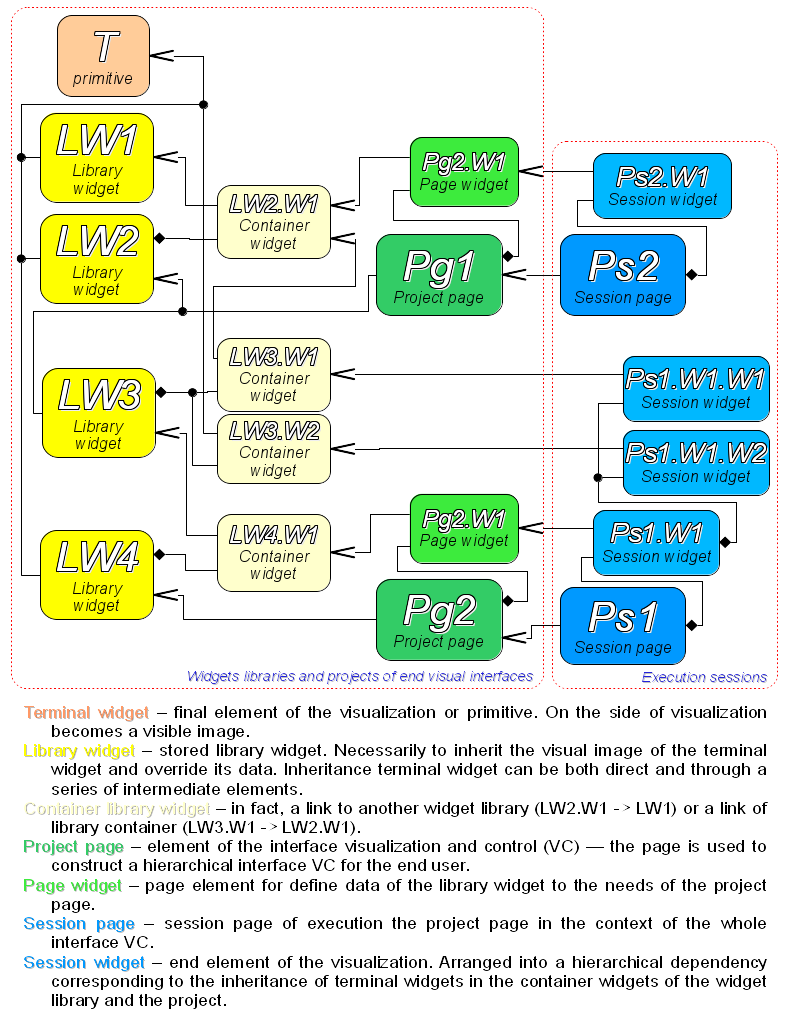
The project session is expanded tree of the project for direct it execution, which includes an individual task of hierarchical the widget's procedures execution. For each project can be opened many sessions. The end-user visual interface forming performs by the visualizers from data of the project's session, after the session creation by the request.
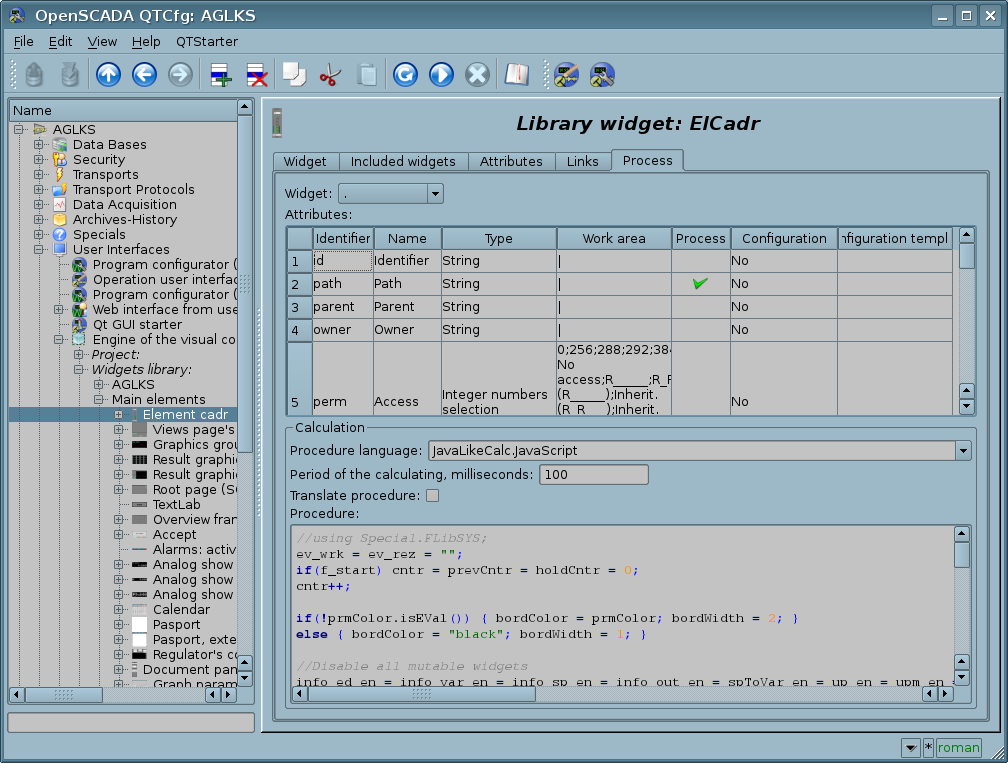
Between the widgets, at different levels of the hierarchy, finally formed fairly complex hereditary links, which are determined by the possibility of using some widgets by others, ranging from the library widget to the session widget. To explain these features of interaction, the figure shows an exhaustive map of "using" inheritance.
At the session level widget contains a object of values of calculation procedure. This object is initiated and used in the case of presence of the calculation procedure itself. At the time of the initialization, the list of parameters of the procedure is created and a compilation of the procedure is performed with these parameters, in the module that implements the selected programming language and with the name of the resulting procedure in the form of a coded full name of the widget. The compiled function is connected to the object of values of the calculation procedure, and further the calculation is performed with the session period.
Calculation and processing of the widget runs in the following sequence:
- the messages available at the time of calculation are selected from the attribute "event" of the widget;
- the events are loaded into the parameter "event" of the object of computation;
- values of the input links are loaded into the object of calculation;
- values of special variables (f_frq, f_start and f_stop) are loaded into the computation object;
- values of selected parameters of the widget are loaded into the object of computation;
- computation;
- uploading the computation object's values to the selected parameters of the widget;
- uploading the events from the parameter "event" of the computation object;
- processing the events and transfer the unprocessed ones at the level above.
The session objects of the project inherit from an abstract object "Widget" and use the appropriate objects of the project. Thus, the session "Session" uses the project "Project" and forms expanded tree on its basis. Project page "Page" is directly used by the session page "SessPage". The remaining objects "SessWdg" are deployed in accordance with the hierarchy of page elements.
In addition to the standard properties of the abstract widget "Widget", elements of the pages and the session pages themselves get the following properties: storage of the object of values of the computational procedure, calculation of the procedures and mechanism for processing of the events. Pages of the session, in addition, contain a container of the following by the hierarchy pages. The session, in general, is calculated with the specified periodicity and in sequence:
- "Page of the top level" -> "Page of the lower level"
- "Widget of the lower level" -> "Widget of the top level"
This policy allows to bypass the pages according to their hierarchy, and events in the widgets "climb up" during one iteration.
The sessions support multi-language at the level of the control interface of OpenSCADA, which depended from values of the generic attributes "lang" and "user" and which visualizer can set in proper way of own language. This function is enabled by dynamic messages translation of OpenSCADA.
3.4 Styles
It knows that people can have individual features in the perception of graphical information. If these features are not taken into account, it is possible to obtain the rejection and abruption of the user to the interface of VC. This rejection and abruption can lead to fatal errors in the management of TP, as well as traumatize the human by the continuous work with the interface. In SCADA systems, arrangements have been made that regulate the requirements for creating the unified UI interface, which is normally perceived by most people. This is practically eliminates the features of people with some deviations.
In order to take this into account and allow centralized and easy to change the visual properties of the interface module is implementing a theme manager of the visualization interface.
User can create many themes, each of which will keep the color, font and other properties of the frame elements. Simple changing of the theme will allow you to change the interface of VC, and the possibility of appointing an individual theme in the user's profile allows to take into account his individual features.
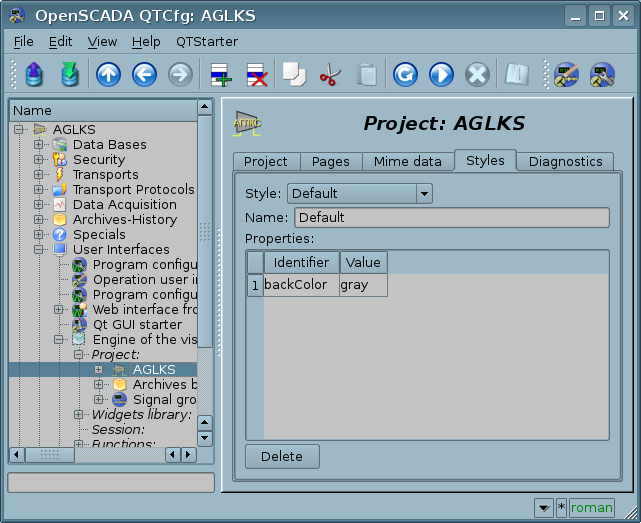
To realize this opportunity, when creating a frame, it is necessary for the properties of color, font and others set the "Configuration" (of the table in the "Process" tab) in the value of "From style". And in the parameter "Configuration template" to specify the identifier of the style field. Next, this field will automatically appear in the style manager and can be modified there. The style manager is available on the project configuration page in the tab "Styles". In this tab, you can the styles create, delete and edit, delete their fields.
In general, the styles are available from the project level. At the level of the widget libraries you can only define the style fields for the widgets. At the project level, at the choice of style, it is started the work with styles, which includes access to the fields of styles instead of direct attribute values. In fact, this means that when reading or writing a widget attribute these operations will be carried out with the corresponding field of the chosen style.
When starting a project, the project-style will be used. In the future, the user can choose a style from the list of available. The user-selected style will be saved and used the next time the project is launched.
3.5 Events, their processing and the events' maps
Given the range of tasks for which OpenSCADA may be used, it is necessary to provide a tool for control of interactive user events. This is due to the fact, that in dealing with individual tasks of embedded systems, input and control devices can greatly vary. But it is enough to look at the regular office keyboard and notebook one, that would remove any doubt about the necessity for the manager of events.
The events manager must work using the maps of events. Events map is a list of named events with indicating its origin. The origin of the events can be a keyboard, mouse, joystick, etc. At an event emerge the events manager is looking for it in the active map and compares with the name of the event. A comparison name of the event is placed in the queue for processing. Widgets in this case must process the given queue of events.
The active map of the events is specified in the profile of each user or it is set by default, in planes.
In general, four types of events are provided:
- events of the VCA shapes-primitives (prefix: ws_), for example, the event of pressing of the screen button — "ws_BtPress";
- keyboard events (prefix: key_) — all events from mouse and keyboard in the form of — "key_presAlt1";
- user events (prefix: usr_) are generated by the user in the procedures of the widgets calculation;
- mapping events (prefix: map_) — events from the events map, in planes.
The event itself does not provide enough information, especially if it is processed at the levels above. To uniquely identify the event and its source, the event in the whole is written as follows: "ws_BtPress:/curtime". Where:
- ws_BtPress — event;
- /curtime — path to the child element that has generated the event.
Table 3.5 provides a list of standard events, the support of which should be provided in visualizers of VCA.
Table 3.5. Standard events
| Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| Keyboard events: key_[pres|rels][Ctrl|Alt|Shift]{Key} | |
| *SC#3b | Scan-code of the key. |
| *#2cd5 | Code of the unnamed key. |
| *Esc | "Esc". |
| *BackSpace | Removing of the previous character — "<--". |
| *Return, *Enter | Enter — "Enter". |
| *Insert | Insertion — "Insert". |
| *Delete | Deleting — "Delete". |
| *Pause | Pause — "Pause". |
| Print of the screen — "Print Screen". | |
| *Home | Home — "Home". |
| *End | End — "End". |
| *Left | To the left — "<-". |
| *Up | To the up — '^'. |
| *Right | To the right — "->". |
| *Down | To the down — '\/'. |
| *PageUp | Page up — "PageUp". |
| *PageDown | Page down — "PageDown". |
| *F1 ... *F35 | Function key from "F1" to "F35". |
| *Space | Space — ' '. |
| *Apostrophe | Apostrophe — '`'. |
| *Asterisk | Asterisk on the additional field of the keyboard — '*'. |
| *Plus | Plus on the additional field of the keyboard — '+'. |
| *Comma | Comma — ','. |
| *Minus | Minus — '-'. |
| *Period | Period — '.'. |
| *Slash | Slash — '\'. |
| *0 ... *9 | Number from '0' to '9'. |
| *Semicolon | Semicolon — ';'. |
| *Equal | Equal — '='. |
| *A ... *Z | Keys of Latin alphabet from 'A' to 'Z'. |
| *BracketLeft | Left square bracket - '['. |
| *BackSlash | Backslash — '/'. |
| *BracketRight | Right square bracket — ']'. |
| *QuoteLeft | Left quote — . |
| Keyboard focus events. | |
| ws_FocusIn | Focus is obtained by the widget. |
| ws_FocusOut | Focus is lost by the widget. |
| Mouse events: | |
| key_mouse[Pres|Rels][Left|Right|Midle] | Pressed/released the mouse button. |
| key_mouseDblClick | Double-click the left mouse button. |
| Events of quietance on the side of the visualizer. | |
| ws_alarmLev | Quietance of all violations by all notices methods and types. |
| ws_alarmNtf{N} | Quietance of all violations by the type {N} (0...7). |
| Events of the elementary figure primitive ElFigure: | |
| ws_Fig[Left|Right|Midle|DblClick] | Activating of the figures (fills) by the mouse button. |
| ws_Fig{N}[Left|Right|Midle|DblClick] | Activating of the figure (fill) N by the mouse button. |
| Events of the form element primitive FormEl: | |
| ws_LnAccept | A new value in the input line is set. |
| ws_TxtAccept | The value of the text editor is changed. |
| ws_ChkChange | The state of the flag is changed. |
| ws_BtPress | The button is pressed. |
| ws_BtRelease | The button is released. |
| ws_BtToggleChange | The button toggle is changed. |
| ws_BtMenu={Item} | Selection of the menu Item on the button. |
| ws_BtLoad | The selected file loaded. |
| ws_CombChange | The value of the combo box is changed. |
| ws_ListChange | The current list item is changed. |
| ws_TreeChange | The current tree item is changed. |
| ws_TableChangeSel | The table item selection is changed. |
| ws_TableEdit_{colN}_{rowN} | The table cell ({colN}:{rowN}) is edited. |
| ws_SliderChange | The slider position is changed. |
| Events of the media content primitive Media: | |
| ws_MapAct{N}[Left|Right|Midle] | Media area with the number N is activated by the mouse button. |
| ws_MediaFinished | Media-stream play is finished. |
Events are the main notification mechanism and are actively used to interact with the user. There are two mechanisms for processing events:
- Primary — the script of management of pages opening.
- Secondary — the computational procedure of the widget.
The mechanism "Script for the control the opening of pages" based on the basic attribute of the widget "evProc", which can be used for opening the pages. Scenario of this attribute is stored as a list of commands with the syntax: "{event}:{evSrc}:{com}:{prm}". Where:
- event — expected event;
- evSrc — path of the nested widget-source of the event;
- com — session command;
- prm — parameter of the command.
The following commands are implemented:
- open — opening page; page to open is specified in the parameter prm both in direct way and as a template, example: /pg_so/1/*/*;
- next — opening of the next page; page to open is specified in the parameter prm as a template, example: /pg_so/*/*/$;
- prev — opening of the previous page; page to open is specified in the parameter prm as a template, example: /pg_so/*/*/$.
Special characters of the template are deciphered as follows:
- pg_so — direct name of the desired-static page (with the prefix), requires the compulsory accordance and is used to identify the last open page;
- 1 — name of a new page in a general way (without a prefix);
- * — the page is taken from the name of a previous opened page or the first available page is substituted, if the previous opened page is missing;
- $ — points the place of the opened page relative to which you are to go to the next or to the previous one.
For a correct understanding of working the template mechanism, when choosing a page, we give a few real examples:
- Changing the signal object:
- Initially: /pg_so/pg_1/pg_mn/pg_1
- Command: open:/pg_so/2/*/*
- Result: /pg_so/pg_2/pg_mn/pg_1
- Switching of the view type:
- Initially: /pg_so/pg_1/pg_mn/pg_1
- Command: open:/pg_so/*/gkadr/*
- Result: /pg_so/pg_1/pg_gkadr/pg_1
- Next/previous page of the view type:
- Initially: /pg_so/pg_1/pg_mn/pg_1
- Command: next:/pg_so/*/*/$
- Result: /pg_so/pg_1/pg_mn/pg_2
As an example, let's give a script to provide the work of the main page of the user interface: </translate>
ws_BtPress:/prev:prev:/pg_so/*/*/$ ws_BtPress:/next:next:/pg_so/*/*/$ ws_BtPress:/go_mn:open:/pg_so/*/mn/* ws_BtPress:/go_graph:open:/pg_so/*/ggraph/* ws_BtPress:/go_cadr:open:/pg_so/*/gcadr/* ws_BtPress:/go_view:open:/pg_so/*/gview/* ws_BtPress:/go_doc:open:/pg_so/*/doc/* ws_BtPress:/go_resg:open:/pg_so/rg/rg/* ws_BtPress:/so1:open:/pg_so/1/*/* ws_BtPress:/so2:open:/pg_so/2/*/* ws_BtPress:/so3:open:/pg_so/3/*/* ws_BtPress:/so4:open:/pg_so/4/*/* ws_BtPress:/so5:open:/pg_so/5/*/* ws_BtPress:/so6:open:/pg_so/6/*/* ws_BtPress:/so7:open:/pg_so/7/*/* ws_BtPress:/so8:open:/pg_so/8/*/* ws_BtPress:/so9:open:/pg_so/9/*/* ws_BtPress:*:open:/pg_control/pg_terminator
<translate> The mechanism "Processing the events with the help of computational procedure of the widget" is based on the attribute "event" and the user procedure of calculating written with the help of the programming language of OpenSCADA. The events, in process of receipt, are accumulated in the attribute "event" till the moment of call of the computational procedure. The computational procedure is called with the specified frequency of calculating the widget and receives the attribute "event" value as the list of events. In the calculation procedure the user can: analyze, process and delete the processed events from the list, and add to the list new events. The remaining, after the procedure execution, and new events are analyzed for compliance with the conditions of the call by means of script of the primary mechanism, after which the remaining events are transmitted to the upper by the hierarchy widget to be processed by it, with the appending of the events path in accordance with the hierarchy of the penetration.
The content of the attribute "event" is a list of events in the format "{event}:{evSrc}", with the event on the separate line. Here is an example of processing events in the Java-like programming language of the OpenSCADA: </translate>
for(ev_rez = "", off = 0; (sval=event.parse(0,"\n",off)).length; ) {
if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_light") alarmSt = 0x1000001;
else if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_alarm") alarmSt = 0x1000002;
else if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_sound") alarmSt = 0x1000004;
else ev_rez += sval+"\n";
}
event = ev_rez;
3.6 Signaling (Alarms)
An important element of any visualization interface is the user notification about the violation — signaling. To simplify the perception, but also in mind the close connectivity of visualization and notification (as a rule, the notification complements the visualization) it is decided to integrate the interface of the notification in the visualization interface. To do this, all the widget provides two additional attributes of the session level: "alarm" and "alarmSt". The attribute "alarm" is used to form the signal by the widget, according to his logic, and the attribute "alarmSt" is used to control the signaling fact of the branch of the session tree.
The "alarm" attribute is a string that has the following format: "{lev}|{categ}|{message}|{type}|{tp_arg}"
Where:
- lev — signaling (alarm) level; number from 0 to 255;
- categ — alarm category; parameter of the acquisition subsystem, object, path, or their combination;
- message — signaling (alarm) message;
- type — type of the notification, is formed as an integer number (0...7), which contains the flags of notification methods; typical notification methods:
- 1 — visual;
- 2 — beep tone, is frequently made through the PC-speaker;
- 4 — sound signal from the sound file or the speech synthesis, and if in the tp_arg the name of the resource of the sound file is specified, then play it, or in other case the speech synthesis from the text specified in message is made.
- tp_arg — argument of the type; often used to directly indicate the resource of a sound signal — a file of sound format, when the sound signal is made.
Attribute "alarmSt" is an integer number that represents the maximum alarm level and the fact of the quietance of the branch of the tree of the session. Format of the number is as follows:
- first byte (0...255) characterizes the level of the alarm of the branch;
- the second byte indicates the type of notification, as well as in the attribute "alarm";
- the third byte indicates the type of notification without quietance, as well as in the attribute "alarm";
- the fourth byte has a special appointment, which is defined by separate bits:
- bit 0 — indicates, by sets, to the quietance fact of the notification into first byte;
- bit 1 — indicates, by sets it and the bit 0, to the quietance return — enable back the quietance.
Alarm forming and receiving of it by the visualizer.
The alarm forming is performed by the widget itself, by setting its own attribute "alarm" in appropriate way and, in accordance with it, the attribute "alarmSt" of the current and the parent widget. Visualizers receive signal notifications using the standard mechanism of notification about changes of the widget attributes.
Taking into account that the processing of the signaling conditions is made in the widgets, the pages containing the objects of signaling should be executed in the background, regardless of their openness to the moment. This is done by setting a flag of the background execution of the page.
Although the mechanism of signaling is built in the visualization area, the possibility of forming non-visual elements of signaling remains, for example, by creating a page that will never open.
Quietance
Quietance — approving process is a fact of the operative personal take its attention to the violation into the TP work. The process mostly means of take actions for the violation eliminating and pressing to the button of the alarm quieting.
Quietance performs by specifying the root of the branch of the widgets and the types of notification, which allows to make quietance on the side of the visualizer, as in groups, for example, on the signaling object, and individually by the object of the source. It is possible to independently quietance different types of alarms. Setting of the quietance is made by the simple modification of the attribute "alarmSt".
Example of the script to work with the signals gives below:
//Separating the fact of the presence of alarms of different methods-types of notification
cvt_light_en = alarmSt&0x100; cvt_alarm_en = alarmSt&0x200; cvt_sound_en = alarmSt&0x400;
//Separating the fact of the presence of alarms without quietance of various ways of notification
cvt_light_active = alarmSt&0x10000; cvt_alarm_active = alarmSt&0x20000; cvt_sound_active = alarmSt&0x40000;
//Processing of the button's events of quietance and the quietance for different ways of notification
for(ev_rez = "", off = 0; (sval=event.parse(0,"\n",off)).length; ) {
if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_light") alarmSt = 0x1000001;
else if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_alarm") alarmSt = 0x1000002;
else if(sval == "ws_BtPress:/cvt_sound") alarmSt = 0x1000004;
else ev_rez += sval + "\n";
}
event = ev_rez;
External notification methods
A first and a typical method of notifications is display's light notification by alarm colors and its dynamic about proper visual elements, which always presents and does not require of specific configuration. But often we need for an external type notification, for example: external lamp, PC buzzer or "howler", arbitrary sound, synthesized speech and etc.
In order to realize this possibility, the external methods of the notification and the corresponding notification types, are freely described for the visualization server and the visualizer itself. On the side of the visualization server, the formation/receipt of the notification resource and the notification itself is described. On the side of the visualizer, the notification is described according to the resources of the visualization server.
Description of the rules and scenarios of the notifications performs with user attributes of the text type for pages of the visualization project, which applies at the page open. That is, potentially, for each open page, you can describe your own rules of the notification, though, it's usually enough and describes the general rules of the notification on the project's main page — a page that opens one-off and does not close at work:
- For the visualization server/engine, by the attribute "notify{N}" into the format:
//flags=notify[{DL}][|resource[|queue[|qMergeMess]]];
if(doRes) { The command text to form the resource. }
if(doNtf) { The command text to notify. }
- For a visualizer by the attribute "notifyVis[Vision|WebVision]{N}" into the format:
//flags=notify[{DL}][|resource[|queue[|quietanceRet]]];
//name={The notifier name}
//ico={The icon name}
{ The notification command text to any or concrete visualizer. }
Flags:
- notify[{DL}] — enables notification with the repeating by the time DL, if the set; for DL = 0 the repeat carried out immediately.
- resource — request-form (force) the notification resource from the visualization server, can be an audio file, a text or other data for the notification produce.
- queue — the notification resources are determined not only by the global sign of alarming and quietance, but also according to the priority sources queue of the notification-resources. The queue is formed on the side of the visualization server, and for the visualizers it is indicated the need to work with it when requesting resources.
- qMergeMess — merging the notifications into the queue by equality their messages.
- quietanceRet — possibility of the visualizer for the quietance recall-return i.e. in fact — the notification enable back.
The exchanging variables:
- en[0,1] — the notification enable (1) or disable (0);
- doNtf[0,1] — call the script of the notification;
- doRes[0,1] — call the script of the resource forming;
- res — content or content's file name of the resource, for the external scripts;
- mess — message-parameters of the forming the resource and the notification.
- lang — language of the current user or system.
The examples and comments to work of the typical notification methods:
- Beep (buzzer) on the visualizer or the visualization server side:
- alarm = "10|Prm||0x02"
- notifyVisVision1 | notify1 =
//flags=notify
if(en) SYS.system("beep -f 1000 -l 1000000 &", true);
else if((beepPID=SYS.system("pidof beep")).toInt()) SYS.system("kill "+beepPID);
- notifyVisVision1 | notify1 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify if test $en = 1; then beep -f 1000 -l 1000000 & else beepPID=$(pidof beep) if test "x$beepPID" != "x"; then kill $beepPID; fi fi
- Repeating play for ready audio file, one common, on the visualizer or the visualization server side:
- alarm = "10|Prm||0x04"
- notify2 | notifyVisVision2 =
//flags=notify2
if(en) SYS.system("play -q alarm.ogg");
- notify2 | notifyVisVision2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2 if test $en = 1; then play -q alarm.ogg; fi
- Play an individual audio file for the source, on the visualization server side:
- alarm = "10|Prm||0x04|res:al_prm1"
- notify2 =
//flags=queue
- notifyVisVision2 =
//flags=notify2|queue
if(doNtf && en && res.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpPlay", res);
SYS.system("play -q tmpPlay");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpPlay");
}
- notifyVisVision2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|queue if test $doNtf = 1 -a $en = 1 -a -s $res; then play -q $res; fi
- Speech synth for an individual message for the source, on the visualizer side:
- alarm = "10|Prm|Text message of the speech synth|0x04"
- notify2 =
//flags=queue
- notifyVisVision2 =
//flags=notify2|queue
if(doNtf && en && mess.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpForSpeech", mess);
SYS.system("festival --tts tmpForSpeech");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpForSpeech");
}
- notifyVisVision2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|queue if test $doNtf = 1 -a $en = 1 -a "x" != "x$mess"; then echo $mess > tmpForSpeech festival --tts tmpForSpeech rm tmpForSpeech fi
- Preparing a sound file, one common, and playing it on the side of the visualizer or the visualization server:
- alarm = "10|Prm||0x04"
- notify2 =
//flags=notify2|resource
if(doRes) res = SYS.fileRead("alarm.ogg"); //Insert here a different method of the generation
if(doNtf && en && res.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpPlay", res);
SYS.system("play -q tmpPlay");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpPlay");
}
- notify2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|resource if test $doRes = 1; then cp -f alarm.ogg $res; fi #Insert here a different method of the generation if test $doNtf = 1 -a $en = 1 -a -s $res; then play -q $res; fi
- notifyVisVision2 =
//flags=notify2|resource
if(en && res.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpPlay", res);
SYS.system("play -q tmpPlay");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpPlay");
}
- notifyVisVision2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|resource if test $en = 1 -a -s $res; then play -q $res; fi
- Prepare an individual audio file for the source of notification through the speech synth, on side of the visualizer or the visualization server:
- alarm = "10|Prm|Text message of the speech synth|0x04"
- notify2 =
//flags=notify2|queue
if(doRes && mess.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpText", mess);
SYS.system("text2wave tmpText -o tmpWAV");
res = SYS.fileRead("tmpWAV");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpText"); SYS.fileRemove("tmpWAV");
}
if(doNtf && en && res.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpPlay", res);
SYS.system("play -q tmpPlay");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpPlay");
}
- notify2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|queue if test $doRes = 1 -a "x" != "x$mess"; then echo $mess > tmpText text2wave tmpText -o $res rm tmpText fi if test $doNtf = 1 -a $en = 1 -a -s $res; then play -q $res; fi
- notifyVisVision2 =
//flags=notify2|queue
if(en && res.length) {
SYS.fileWrite("tmpPlay", res);
SYS.system("play -q tmpPlay");
SYS.fileRemove("tmpPlay");
}
- notifyVisVision2 =
#!/bin/sh #flags=notify2|queue if test $en = 1 -a -s $res; then play -q $res; fi
3.7 Rights management
For the separation of access to the interface of VC and its components, every widget contains information about the owner, its groups and access rights. Access rights are recorded, as adopted in OpenSCADA, as a triad: "{user}{group[,group1,groupN]}{other}", where each element consists of two attributes of the access, for which the following interpretation is adopted:
- r — the right to review the widget;
- w — the right to control over the widget.
In the development mode a simple scheme of accessing "root.UI:RWRWR_" is used, which means — all users can open and view the libraries, their components and projects, and all users of the group "UI" (user interfaces) can edit.
In the runtime mode the rights work, described in the interface components, which include the ability to inherit the owner and rights from the top to the bottom. Wherein, by default, the inheritance enabled for each widget, then they get the owner and the rights of the project. At the same time, the direct setting of the rights of the complex widget will propagate them to all components of this widget.
3.8 Linkage with the dynamics
To provide the visualization interface of relevant data, data from the subsystem "Data acquisition (DAQ)" should be used. The nature of these data is as follows:
- parameters that contain some number of attributes;
- attributes of the parameter can provide information of five types: Boolean, Integer, Real, String and Object;
- attributes of the parameter can have their archive (history);
- attributes of the parameter can be set to read, write and with full access.
Given the first point, it is necessary to provide the possibility of group-based reference. To do this, we use the logical level concept.
According to point 2, the links provide a transparent type conversion and do not require a special configuration.
To satisfy the opportunities for accessing to archives, in accordance with the item 3, links make check of the attribute type, and in the case of connection to the "Address", the address of the link is put into the value.
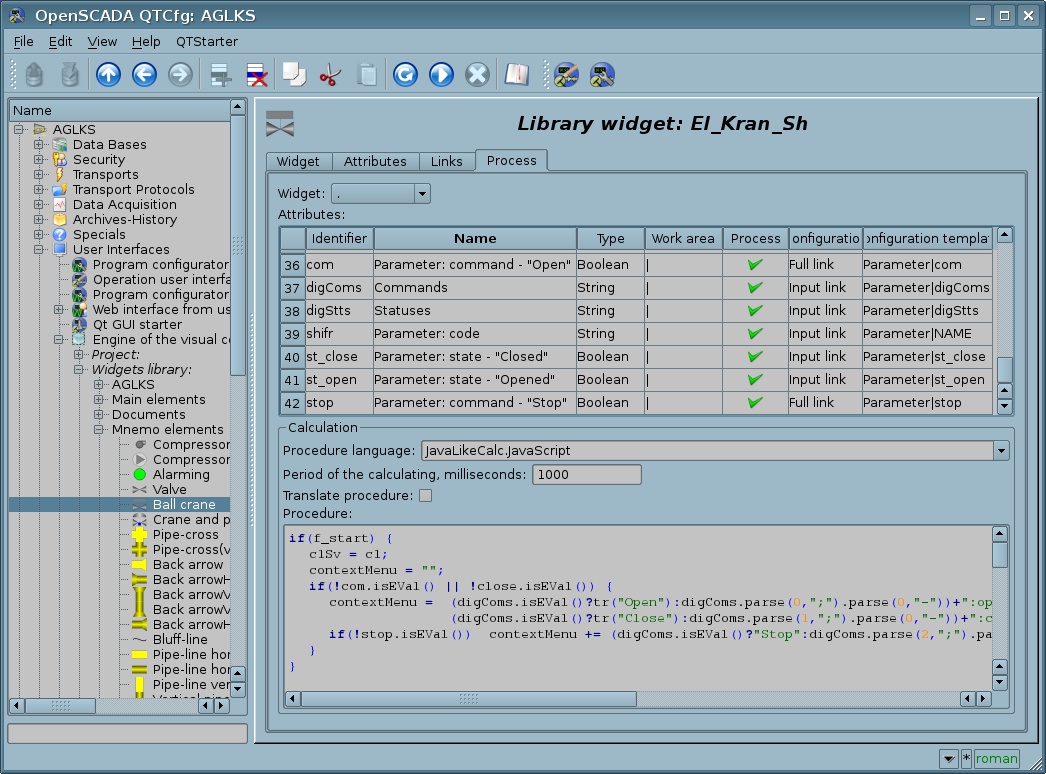
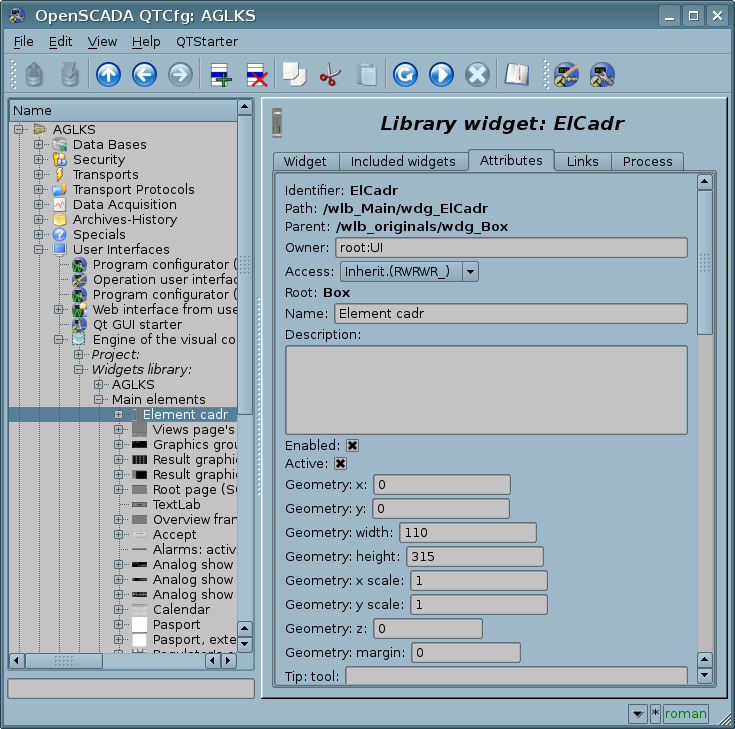
In the VCA terms, the dynamic links and configuration of the dynamics are the one process, to describe a configuration of which the tab "Processing" of the widgets is provided. The tab contains a table of configuration of the attributes properties and the calculation procedure text of the widget.
In addition to configuration fields of the attributes the column "Processing" in the table provides, for selective using of the attributes in the computational procedure of the widget, and the columns "Configuration", "Configuration template", to describe the links configuration.
If the "Processing" column is true, then the variable {widget ID}_{attribute ID} becomes available in the computational procedure, for example cw_value.
The column "Configuration" allows to specify the link type of the widget attribute:
- Constant — in the tab of widget links the field for indication of a constant appears, for example, of the special color or header of the template frames.
- Input link — linkage with the dynamics for read-only.
- Output link — linkage with the dynamics just for writing.
- Full link — complete linkage with dynamic, read/write.
- From style — take the value from the project's style.
The column "Configuration template" makes it possible to describe the groups of dynamic attributes. For example, it may be different types of parameters of the subsystem "DAQ" and other interface widgets. With the correct formation of this field, the mechanism of automatic assignment of attributes is worked, with only the parameter of the subsystem "DAQ" or the widget of the interface, which simplifies and accelerates the configuration process. Value of this column has the following format:
- For constant: direct the attribute value.
- For link: "{parameter}|{identifier}", where:
- parameter — group of the attribute;
- identifier — identifier of the attribute; same the value is compared with the attributes of the DAQ parameters with automatic linkage, after the group link indication.
- For style: identifier-name of the style field.
There may be several types of links, that are defined by the prefix:
- val: — Direct download value through the link mechanism. For example, the "val:100" link loads value 100 to the widget attribute. Often used in the absence of a terminal point of linking, for the purpose of directly setting the value.
- prm: — Link to the parameter attribute or parameter, in general, for the attributes group of the "Data acquisition" subsystem. For example, the link "prm:/LogicLev/experiment/Pi/var" performs the access of the widget attribute to the parameter attribute of the subsystem "Data acquisition". Sign "(+)" at the end of the address indicate about successful linking and presence of the target. For object-type attributes, permissible hierarchical access to a specific property of the object, by specifying its path through the symbol '#', for example: "prm:/LogicLev/experiment/Pi/var#pr1/pr2".
- wdg: — Link to the attribute of another widget or widget, in general, for the attributes group. For example, the link "wdg:/ses_AGLKS/pg_so/pg_1/pg_ggraph/pg_1/a_bordColor" performs the access of the attribute of one widget to the attribute of another one. Supported both absolute and relative paths of the links. The reference point of the address of the absolute link is the root object of the module "VCAEngine", which means — the first element of the absolute address is ID of the session or project. The first element, on the side of the session, drops, so the links, installed in the project, work there. Relative links take a countdown from the widget where the link is specified. A special element of relative link is an element of a higher node "..".
- arh: — A special type of the link, available only for a separate attribute of the type "Address", which allows you to connect directly to the value archive ("arh:CPU_load"). It may be useful to specify the archive as a data source for the primitive "Diagram".
Processing of the links occurs at a period of the widget calculating in the following order:
- receiving the data from the input links;
- performing the calculation of the widget procedure;
- transmission the values by the output links.
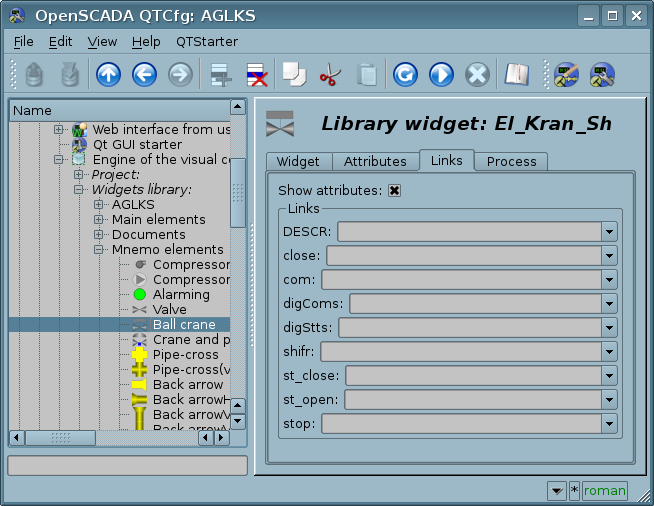
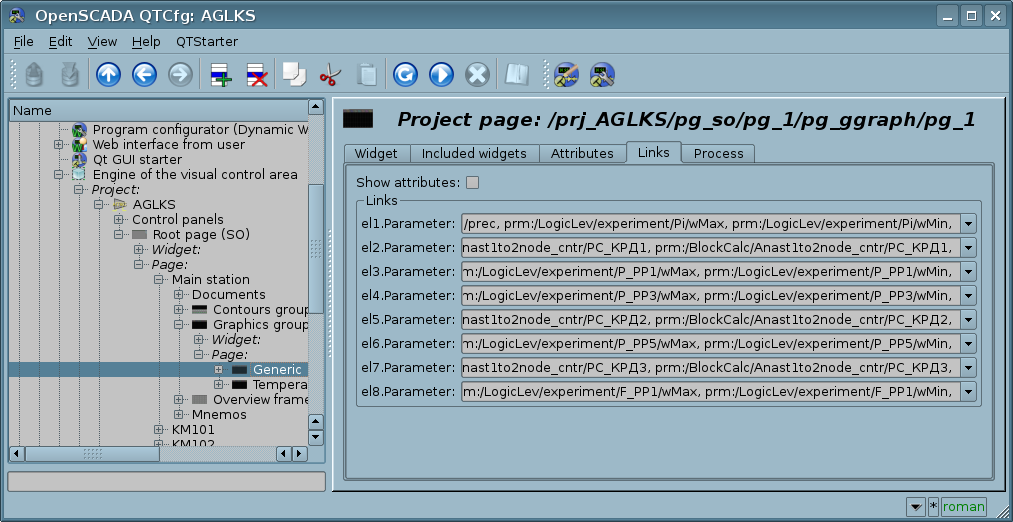
The figure shows a tab of links for group attributes, by specifying only the parameter. The following figure shows the individual attribute assignment.
When placing a widget in the widget container, all links of the original widget are added to the list of resulting links of the widget container, however, only to a depth at one level of nesting.
From the foregoing it is clear that the links are set by the user during the configuration of the interface. However, in order to allow the creation of general-purpose frames with the function of providing detailed data of different sources of the same type, a dynamic linking mechanism is required. Such a mechanism is foreseen:
- reserving the key identifier "<page>" for the group of attributes of links in general purpose frames;
- dynamically assigning links to the identifier "<page>" in the process of opening a general-purpose frame by the signal from another widget.
Let's examine the example when we have the frame of general-purpose "Control panel of graph" and a lot of "Graphs" in different frames. "Control panel of graph" has links with the templates:
- tSek -> "<page>|tSek"
- tSize -> "<page>|tSize"
- trcPer -> "<page>|trcPer"
- valArch -> "<page>|valArch"
In this case, each widget "Graph" has attributes "tSek", "tSize", "trcPer" and "valArch". Calling the "Control panel of graph" by opening signal from any widget "Graph", the attributes of the "Control panel of graph" are linked together with the attributes of the "Graph" widget, according to the template. As a result, all changes in the "Control panel of graph" will be displayed on the graph, through these links.
If the "Graph" widget has external links to the parameters of the "Data acquisition" subsystem, the "Control panel of graph" links will be installed on the external source. Additionally, if the "Control panel of graph" will be declared the links to the missing attributes directly in the widget "Graph", then the search will be made for the presence of such attributes in the external source — the first one on which a direct link is established, performing, thereby, the addition of the missing links.
To visualize this mechanism the table is provided.
Table. The mechanism of the dynamic linkage.
| Attributes of the "Control panel of graph" (the template of dynamic linkage) | "Graph" attributes | Attributes of the external "Parameter" | Resulting link or value of the linking attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| tSek (<page>|tSek) | tSek | - | "Graph".tSek |
| tSize (<page>|tSize) | tSize | - | "Graph".tSize |
| trcPer (<page>|trcPer) | trcPer | - | "Graph".trcPer |
| valArch (<page>|valArch) | valArch | - | "Graph".valArch |
| var (<page>|var) | var | var | "Parameter".var |
| ed (<page>|ed) | - | ed | "Parameter".ed |
| max (<page>|max) | - | - | EVAL |
| min (<page>|min) | - | - | EVAL |
3.9 Primitives of the widgets
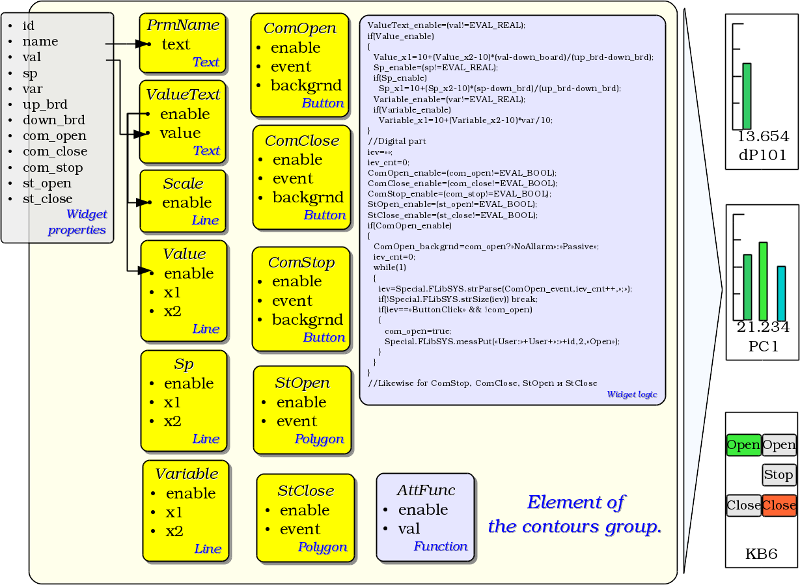
Any newly created widget is based on one of several primitives — end element of the visualization, by installing of the kinship as directly to the primitive, as well as through the several intermediate user widgets. Each of the primitives contains a mechanism of the data model. An instance of the widget stores the properties values of the primitive own configuration.
The tasks of the visualization interface include support and work with the data model of the widgets primitives. The widgets primitives should be thoroughly worked out and unified, in order to capture as many opportunities as possible in a smaller number of poorly linked, with the purpose, primitives.
Table. Library of the primitives of the widgets — basic elements of the visualization.
| Identifier | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| ElFigure | Elementary graphical figure |
The primitive is the basis for drawing elementary graphical shapes with their possible combinations in a single object. The support of the following elementary figures is provided:
For all the figures, contained in the widget, set the common properties of thickness, color, etc., provides the possibility to specify the above-mentioned attributes for each figure separately and their dynamization. |
| FormEl | Element of the form |
Includes support for the standard form components:
|
| Text | Text | Text element-label. Characterized by the font type, color, orientation and alignment. Support for arguments is provided. |
| Media | Media | Element of the visualization of raster and vector images of various formats, playback of the animated images, playback of the audio fragments and view of the video fragments. |
| Diagram | Diagram | Element of the diagram with the support of the visualization in the real-time for the flow of several: trends (time charts), spectrum, XY diagrams. |
| Protocol | Protocol | Element of the protocol — visualizer of the program messages, with support of the multiple operating modes. |
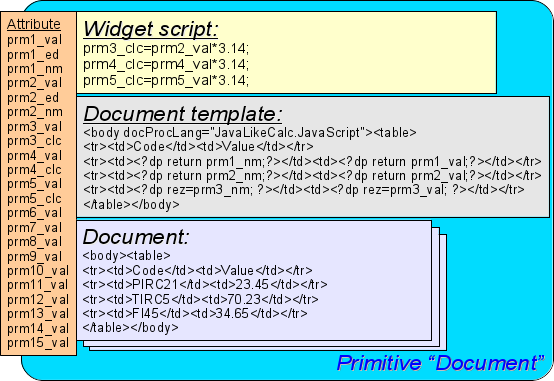
| Document | Document | Element of the generating reports, journals and other documentation on the basis of available data. |
| Box | Container | Contains the mechanism for other widgets placement-including with the purpose of creation of new, more complex, widgets and pages of the end visualization. |
| Function, in plane | Function of API of the object model of OpenSCADA | Not visual widget, on the runtime side, which allows to include a computing function of the object model of OpenSCADA in the VCA. |
Table. The common set of properties/attributes in the widget
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | Identifier | - | Identifier of the element. The attribute is read-only, designed to provide information on the ID of the element. |
| path | Path | - | Path to the widget. The attribute is read-only and designed to provide full information about the element location. |
| parent | Parent | - | Path to the parent widget. The attribute is read-only and designed to provide information about the ancestor location which the widget is inherited from. |
| owner | Owner | - | The widget owner and group in the view "{owner}:{group[,group1,groupN]}", by default the "root:UI". |
| perm | Permission | - |
Permission to the widget in the view "{user}{group}{other}" plus the inheritance flag, enables the inheritance for owner and its permissions from the upper widget.
By default the 01000 — inheritance. |
| root | Root | 1 | Identifier of the widget-primitive (basic element) which underlies the widget visualization shape. |
| name | Name | - | Name of the element. Accessible to modification the element name. |
| dscr | Description | - | Description of the element. Text field of the brief description. |
| en | Enabled | 5 | The state "Enabled" of the element. Disabled element is not shown in the execution mode. |
| active | Active | 6 | The state "Active" of the element. Active element may receive focus in the execution mode, and thus receive keyboard and other events with their subsequent processing. |
| geomX | Geometry: x | 7 | Geometry, coordinate 'x' of the element position. |
| geomY | Geometry: y | 8 | Geometry, coordinate 'y' of the element position. |
| geomW | Geometry: width | 9 | Geometry, the width of the element. |
| geomH | Geometry: height | 10 | Geometry, the height of the element. |
| geomXsc | Geometry: x scale | 13 | Horizontally scale of the element. |
| geomYsc | Geometry: y scale | 14 | Vertical scale of the element. |
| geomZ | Geometry: z | 11 | Geometry, coordinate 'z' (level) of the element on the frame. Defines also the order to transfer the focus through active elements. |
| geomMargin | Geometry: margin | 12 | Geometry, the margins of the element. |
| tipTool | Tip: tool | 15 | Text of a brief help or tip on this element. Realized usually as a tool tip, while keeping your mouse cursor over the element. |
| tipStatus | Tip: status | 16 |
Text information on the status of the element or the guide to action over the element. Implemented usually in the form of a message in the status bar while keeping your mouse cursor over the element.
|
| contextMenu | Context menu | 17 |
Context menu in the strings list view: "{ItName}:{Signal}".
|
| evProc | Events processing | - |
Attribute for storing of the script of the events processing for direct control of the user interface. Script is a list of commands to the visualization interface, generated at the event receipt (attribute event). Direct events processing to manage pages, in the view: "{event}:{evSrc}:{com}:{prm}". Where:
Examples:
|
| Additional attributes for items, placed into the project in the role of a page. | |||
| pgOpen | Page: opened | - |
Sign "The page is opened".
|
| pgNoOpenProc | Page: process not opened | - | Sign "Execute the page, even if it is closed". |
| pgOpenSrc | Page: source of the opening | 3 |
Full address of the page which has opened this one.
|
| pgGrp | Page: group | 4 | group of the pages. |
| Additional attributes of the execution mode — by the session. (Virtual attributes are not available in the widget procedure) | |||
| event | Events | - | Special attribute of the collection of events of the widget in the list, which is divided by the new line. Access to the attribute is protected by a critical section in order to avoid loss of the events. The attribute is always available in the widget procedure. |
| load | Load | -1 | Virtual command of the group data download. |
| focus | Focus | -2 | Special attribute of the indicating the fact of receiving the focus by an active widget. Attribute of the widget and of the included widgets is available in the widgets procedures. |
| perm | Permission | -3 | Virtual attribute of the rights of the active user to view and control the widget. |
- * — Special function of the widget attribute which executing in the project session at any user's modification.
The engine of the visualization environment provides activation of the visualizer specific attributes. The activation process performs at opening a session of the project and means for the project: creation of the specific attribute with the specified properties, at case it lack, and activation for tracing its modification by the engine of the visualization environment, like to the attributes of forming primitive's shapes. For the specific attributes list of the visualizer you can see the documentation of the proper visualizer.
3.9.1 Elementary graphical figure (ElFigure)
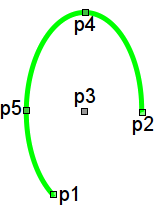
The primitive is the basis for drawing basic graphical shapes with their possible combinations in a single object. Taking into account the wide range of various shapes, which must be maintained by the primitive, and at the same time the primitive must be simple enough for using and, if possible, for implementation, it was decided to limit the list of the basic figures used for the construction of the resulting graphics to these figures: line, arc, Bézier curve and fill of the enclosed spaces. Based at these basic figures, it is possible to construct derived figures by combining the basic. In the context of the primitive, there is a possibility to set the transparency of the color in the range [0...255], where '0' — complete transparency.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Elementary figure (ElFigure)"
3.9.2 Element of the form (FormEl)
A primitive, designed to provide the user with standard elements of the form. The general attribute list depends on the element type.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Element of the form (FormEl)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| elType | Element type | 20 | Type of the element, from which depends the list of additional attributes:
|
| Line edit: | |||
| value | Value | 21 | Contents of the line. |
| view | View | 22 | View of the editing line:
|
| cfg | Configuration | 23 | Configuration of the line. Format of the value of the field for different views of the lines:
|
| confirm | Confirm | 24 | Enable the confirming mode. |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}", where:
Examples:
|
| Text edit: | |||
| value | Value | 21 | Content of the editor. |
| wordWrap | Word wrap | 22 | Automatically wrap text by words. |
| confirm | Confirm | 24 | Enable the confirming mode. |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (details above). |
| Check box: | |||
| name | Name | 26 | Name/label of the checkbox. |
| value | Value | 21 | Value of the checkbox. |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (details above). |
| Button: | |||
| name | Name | 26 | Name-inscription on the button. Allowed symbols '\n' for multiple line names. |
| value | Value | 21 | The value, different for modes:
|
| img | Image | 22 | Image on the button. Image name in the view [{src}:]{name}, where:
Examples:
|
| color | Color | 23 | Color of the button. Color name form "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| colorText | Color:text | 27 | Color of the text (details above). |
| mode | Mode | 24 | Operation mode of the button:
|
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (details above). |
| List: | |||
| value | Value | 21 | Current value of the list. |
| items | Items | 22 | Entries of the list. |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (details above). |
| mult | Multiple selection | 23 | Allow for multiple entries selection of the list. |
| Combo box, Tree: | |||
| value | Value | 21 | Current value of the list. |
| items | Items | 22 | Entries of the list or hierarchical items list of the tree in path "/{DIR}/{DIR}/{ITEM}". |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (details above). |
| Table: | |||
| set | Setting value | 23 | Value of edition of a cell of the table which address into the event "ws_TableEdit_{colN}_{rowN}". |
| value | Value | 21 | Address of the selected item. It changing follows by the event "ws_TableChangeSel". The address format depends from the table's selection mode:
|
| items | Elements | 22 |
The table structure and content in the XML view:
<tbl>
<h><s>{Header1}</s><s>{Header2}</s></h>
<r><s>{Row1Column1String}</s><i>{Row1Column1Integer}</i></r>
<r><b>{Row2Column1Logical}</b><r>{Row2Column2Real}</r></r>
</tbl>
The tags:
|
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the form "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}" (the details above). |
| Slider and Scroll Bar: | |||
| value | Value | 21 | Slider position. |
| cfg | Configuration | 22 | Configuration of the slider in the format: "{VertOrient}:{Min}:{Max}:{SinglStep}:{PageStep}". Where:
|
3.9.3 Text element (Text)
This primitive is intended for outputting plain and HTML text used as labels and different signatures. In order to create decorations, primitive supports the surrounding of the text by frame.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Text element (Text)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| backColor | Background: color | 20 | Background color. Color name in the view "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| backImg | Background: image | 21 | Background image. The image name in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| bordWidth | Border: width | 22 | Border width. |
| bordColor | Border: color | 23 | Border color (details in attribute 20). |
| bordStyle | Border: style | 24 | Border style: "None", "Dotted", "Dashed", "Solid", "Double", "Groove", "Ridge", "Inset", "Outset". |
| font | Font | 25 | Font name in the view "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}", where:
Examples:
|
| color | Color | 26 | Text color (details in attribute 20). |
| orient | Orientation angle | 27 | Orientation of the text, the angle of rotation. |
| wordWrap | Word wrap | 28 | Automatically wrap text by words. |
| alignment | Alignment | 29 | Alignment of the text: "Top left", "Top right", "Top center", "Top justify", "Bottom left", "Bottom right", "Bottom justify", "V center left", "V center right", "Center", "V center justify". |
| inHtml | In HTML | 31 | Displays and supports the content of the argument text in HTML. |
| text | Text | 30 | Text value. Use "%{x}" to place the value of the argument 'x' (from 1). |
| numbArg | Arguments number | 40 | Arguments number. |
| Attributes of the arguments | |||
| arg{x}val | Argument {x}: value | 50+10*x | Argument x value. |
| arg{x}tp | Argument {x}: type | 50+10*x+1 | Argument x type: "Integer", "Real", "String". |
| arg{x}cfg | Argument {x}: config | 50+10*x+2 | Argument x configuration:
|
3.9.4 Element of visualization of media-materials (Media)
This primitive is intended for playing various media materials, ranging from simple images to high-quality audio and video streams.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Element of visualization of media-materials (Media)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| backColor | Background: color | 20 | Background color. Color name in the view "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| backImg | Background: image | 21 | Background image. The image name in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| bordWidth | Border: width | 22 | Border width. |
| bordColor | Border: color | 23 | Border color (details in attribute 20). |
| bordStyle | Border: style | 24 | Border style: "None", "Dotted", "Dashed", "Solid", "Double", "Groove", "Ridge", "Inset", "Outset". |
| src | Source | 25 |
Name of the Media source in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| type | Type | 27 |
Media type:
|
| areas | Map areas | 28 | Number of the active areas. |
| Attributes of the image (Image) | |||
| fit | Fit to the widget size | 26 | Sign "Coordinate the contents with the widget size". |
| Attributes of the video (Movie) | |||
| fit | Fit to the widget size | 26 | Sign "Coordinate the contents with the widget size". |
| speed | Play speed | 29 | Speed of playback, as a percentage from the original speed. If the value is less than 1%, the playback stops. |
| Attributes of the full video (Full video) | |||
| play | Play | 29 | Video/audio — "Play". |
| roll | Roll play | 30 | Roll play on the finish. |
| pause | Pause | 31 | Playing pause. |
| size | Size | 32 | Total video size, in milliseconds. |
| seek | Seek | 33 | Seek video playing, in milliseconds. |
| volume | Volume | 34 | Sound volume [0...100]. |
| Active areas | |||
| area{x}shp | Area {x}: shape | 40+3*x | Type of the area x: "Rect", "Poly", "Circle". |
| area{x}coord | Area {x}: coordinates | 40+3*x+1 | Coordinates of the area x, are separated by commas: "x1,y1,x2,y2,xN,yN". |
| area{x}title | Area {x}: title | 40+3*x+2 | Title of the area x. |
3.9.5 Element of constructing diagrams (Diagram)
This primitive targeted to construct various diagrams in the time, including graphs-trends showing ongoing process and the archive data. Following types of the diagrams are implemented:
- "Graph-trend" — builds a graph of the parameter values in the time.
- "Spectrum" — builds the frequency spectrum of the parameter values. Window of the data of the frequency spectrum is formed on the basis of the horizontally size of the widget, in pixels, and the available data of the parameters imposed on the grid of the horizontal size. Due to this, the minimum allocated frequency is determined by the value of the attribute "tSize" — "1/tSize", and the maximum one is determined by half-width of the graph in pixels multiplied by the minimum frequency "width/(2*tSize)".
- "XY" — builds the two-dimensional graph of the parameters values, by pairs to one graphic, where paired by axis Y (0,2,4...) and unpaired by axis X (1,3,5...). Specified data time range is used in the received values of the parameters of the X and Y axis, with the subsequent imaging.
For all the diagram types possible to set, as the data source:
- parameter of the subsystem "DAQ";
- value archive;
- direct data block from the user.
The tracking mode is supported for current values and values from the archive, and it is possible to construct graphs of parameters that do not have a value archive by accumulating the current values in the buffer of the diagram and only at the moment of active display of this diagram.
Process of access to archival data is optimized by introducing an intermediate buffer of displaying, as well as the packaging of data traffic upon request, by bringing the data to a quality sufficient to display.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Element of constructing diagrams (Diagram)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| backColor | Background: color | 20 | Background color. Color name in the view "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| backImg | Background: image | 21 | Background image. The image name in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| bordWidth | Border: width | 22 | Border width. |
| bordColor | Border: color | 23 | Border color (details in attribute 20). |
| bordStyle | Border: style | 24 | Border style: "None", "Dotted", "Dashed", "Solid", "Double", "Groove", "Ridge", "Inset", "Outset". |
| trcPer | Tracing period, seconds | 25 | Mode and periodicity of the tracing. |
| type | Type | 26 | Diagram type: "Trend", "Spectrum", "XY". |
| General attributes for all the types | |||
| tSek | Time: seconds | 27 | Current time, seconds. |
| tUSek | Time: microseconds | 28 | Current time, microseconds. |
| tSize | Size, seconds | 29 | Size of the data, seconds. |
| curSek | Cursor: seconds | 30 | Cursor position, seconds. |
| curUSek | Cursor: microseconds | 31 | Cursor position, microseconds. |
| curColor | Cursor: color | 32 | Cursor color. |
| sclColor | Scale: color | 33 | Color of the scale-grid (details in attribute 20). |
| sclHor | Scale: horizontal | 34 | Horizontal mode of the scale-grid: "No draw", "Grid", "Markers", "Grid and markers", "Grid (log)", "Markers (log)", "Grid and markers (log)". |
| sclHorScl | Scale: horizontal scale (%) | 44 | Horizontal scale of the graphic in percents, exclusively for the type "XY". |
| sclHorSclOff | Scale: horizontal scale offset (%) | 45 | Offset of the horizontal scale of the graphic in percents, exclusively for type "XY". |
| sclVer | Scale: vertical | 35 | Vertical mode of the scale-grid: "No draw", "Grid", "Markers", "Grid and markers", "Grid (log)", "Markers (log)", "Grid and markers (log)". |
| sclVerScl | Scale: vertical scale (%) | 40 | Vertical scale of the graphic in percents. |
| sclVerSclOff | Scale: vertical scale offset (%) | 41 | Offset of the vertical scale of the graphic in percents. |
| sclMarkColor | Scale: Markers: color | 36 | Color of the markers of the scale-grid (details in attribute 20). |
| sclMarkFont | Scale: Markers: font | 37 | Font of the markers of the scale-grid. Font name in the view "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}", where:
Examples:
|
| valArch | Value archiver | 38 | Value archiver in the view "{ArchMod}.{ArchivatorId}". |
| valsForPix | Values per pixel | 42 | Number of values per pixel. Increase to enhance the accuracy of export at the large time intervals. |
| parNum | Parameters number | 39 | Number of parameters that can be displayed on the one trend. |
| Attributes for type: "Graph" | |||
| sclHorPer | Scale: horizontal grid size, seconds | 43 | Fixed period of the horizontal scale grid — disables automatic calculation of the grid period. Activates if the number of periods for a total size greater than two and a size of one period is at least 15 pixels. |
| Individual attributes of the parameters | |||
| prm{X}addr | Parameter {X}: address | 50+10*{X} | Full address to a DAQ attribute of the parameter X or to an archive. Direct data set by the prefixes is supported:
Example:
|
| prm{X}bordL | Parametr {X}: view border: lower | 50+10*{X}+1 | Lower limit of the parameter X. |
| prm{X}bordU | Parametr {X}: view border: upper | 50+10*{X}+2 | Upper limit of the parameter X. |
| prm{X}color | Parametr {X}: color | 50+10*{X}+3 | Color for display the chart of the parameter X (details in attribute 20). |
| prm{X}width | Parametr {X}: width | 50+10*{X}+6 | Line width for display the chart of the parameter X, in pixels. |
| prm{X}scl | Parametr {X}: scale | 50+10*{X}+5 | Separated vertical scale mode of the parameter X: "Global", "Markers", "Grid and markers", "Markers (log)", "Grid and markers (log)". |
| prm{X}val | Parametr {X}: value | 50+10*{X}+4 | Value of the parameter X under the cursor. |
| prm{X}prop | Parametr {X}: properties | 50+10*{X}+7 | Real archive properties in the view "{BegArh}:{EndArh}:{DataPeriod}", where "BegArh", "EndArh", "DataPeriod" — begin, end and period of the archive's data, in seconds, in real up to microseconds (1e-6). |
3.9.6 Element of building the protocols based on the message archives (Protocol)
This primitive is designed to visualize the data of the message archive through the formation of protocols with different ways of visualization, starting from a static scanning view and finishing with dynamic tracing.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Element of building the protocols based on the message archives (Protocol)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| backColor | Background: color | 20 | Background color. Color name in the view "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| backImg | Background: image | 21 | Background image. The image name in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| font | Font | 22 | Font name in the view "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}", where:
Examples:
|
| headVis | Header visible | 23 | Visibility for header of the table. |
| time | Time, seconds | 24 | Current time, seconds. |
| tSize | Size, seconds | 25 | Query data size, seconds. Set value to '0' for get all alarms, for "lev" < 0. |
| trcPer | Tracing period, seconds | 26 | Mode and periodicity of the tracing. |
| arch | Archiver | 27 | Message archiver in the view "{ArchMod}.{ArchivatorId}". |
| tmpl | Template | 28 | Category template or regular expression "/{re}/". For the template the special symbols are reserved:
|
| lev | Level | 29 | Level of the messages. Set value to < 0 for get the current alarms. |
| viewOrd | View order | 30 | View order: "By time", "By level", "By category", "By messages", "By time (reverse)", "By level (reverse)", "By category (reverse)", "By messages (reverse)". |
| col | Show columns | 31 | List of the visible and order of the columns separated by the symbol ';'. The columns are provided:
|
| itProp | Item properties | 32 | Number of the item properties. |
| Individual attributes of the item properties | |||
| it{X}lev | Item {X}: level | 40+5*{X} | Criterion: level of the element X, more or equal for the pointed. |
| it{X}tmpl | Item {X}: template | 40+5*{X}+1 | Criterion: category template of the element X (details in attribute 28). |
| it{X}fnt | Item {X}: font | 40+5*{X}+2 | Font of the element X (details in attribute 22). |
| it{X}сolor | Item {X}: color | 40+5*{X}+3 | Color of the element X (details in attribute 20). |
3.9.7 Element of formation of the documentation (Document)
The primitive is intended for the formation of reporting, operational and other documentation based on document templates.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Element of formation of the documentation (Document)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| style | CSS | 20 | CSS rules in lines like to "body { background-color:#818181; }". |
| tmpl | Template | 21 | Template of the document in XHTML, starts from the tag "body" and includes the procedure parts:
<body docProcLang="JavaLikeCalc.JavaScript"> <h1>Value<?dp return wCod+1.314;?></h1> </body> |
| doc | Document | 22 | Final document in XHTML, starts from the tag "body". |
| font | Font | 26 | Basic font of the text. Font name in the view "{family} {size} {bold} {italic} {underline} {strike}", where:
Examples:
|
| bTime | Time: begin | 24 | Start time of the document, seconds. |
| time | Time: current | 23 | Time of the document generation, seconds. Write the time for the document generation from that point or zero for regeneration. |
| process | In the process | 27 | Indication of the process of forming a document in a separate thread. |
| n | Archive size | 25 | Number of the documents or the depth of the archive. |
| Attributes of the enabled archival mode | |||
| aCur | Archive: cursor: current | - | Position of the current document in the archive. Record of the value <0 produces the archiving of this document. |
| vCur | Archive: cursor: view | - |
Current visual document of the archive. Writing a value of:
|
| aDoc | Archive: current document | - | Current archive document in XHTML, starts from the tag "body". |
| aSize | Archive: size | - | Real size of the archive document. |
Features of the primitive "Document":
- Flexible formation of document structure based on HyperText Markup Language, which provides support for a wide range of features in the documents formatting.
- Formation of the documents at a command or a schedule, which necessary for creation of reports to the archive and then reviewing the archive.
- Formation of the documents in real time, to provide them completely dynamically and on the basis of archives at the specified time.
- Using the widget attributes for transmission to the document of values and addresses to the archives, which allows you to use the document widget as a template when generating reports with other input data.
The basis of any document is the XHTML template. The XHTML-template is the tag "body" of the WEB-page which contains the document's static in the standard XHTML 1.0 and elements of the executable instructions in the user programming language of OpenSCADA in the view <?dp {procedure} ?>. The resulting document is formed by the procedures execution and insertion of their result into the document.
The source for values of the executable instructions are the widget attributes of the primitive, as well as all the mechanisms of the user programming language OpenSCADA. Attributes may be added by the user and they can be linked to the actual attributes or parameters or they can be autonomous, values of which will be formed in the widget procedure. In the case of linked attributes the values can be extracted from the archive-history.
The figure shows the structure of the widget of the primitive "Document". According to this structure, "Document" contains: XHTML template, results documents and data processing procedure. Data source of the procedure and output documents is attributes of the widget.
Working in two modes is provided: "Dynamic" and "Archive". Difference between archive mode is the availability of the archive of the specified depth and attributes which allow you to control the process of archiving and viewing of the document in the archive.
Generation of the document is always performed at the time of setting of the attribute time relative to the earlier set begin time of the document in the attribute bTime. With the archive turned off the resulting document is placed directly in the attribute doc. When the archive is turned on the resulting document is placed in the cell under the cursor, the attribute aCur, as well as in doc if value of the archive cursor aCur and the visualized document cursor vCur match. Attributes of the archival cursors provide several command values:
- "aCur < 0" — moves the archiver cursor to the following position, thereby leaving the previous document in the archive and clearing the document under the cursor, at short the circle archive.
- "vCur == -1" — selecting the next document to be displayed, the selected document is copied to the attribute doc.
- "vCur == -2" — selecting the previous document to be displayed, the selected document is copied to the attribute doc.
As mentioned above, the dynamics of the document template is determined by inserts of executable instructions of the view "<?dp {procedure} ?>". The procedures may use the same attributes of the widget and functions of the user programming interface of OpenSCADA. In addition to widget attributes, special attributes are reserved, see the table.
Table 3.8.7.a. Special and reserved elements of the template.
| Name | Assignment |
|---|---|
| Attributes | |
| rez | Attribute of the result of the procedure, the contents of which is placed in the document tree. |
| lTime | Last formation time. If the document is formed for the first time, lTime is equal to the bTime. |
| rTime | Contains the time of look through values, seconds, defined within tags with the attribute docRept. |
| rTimeU | Contains the time of look through values, microseconds, defined within tags with the attribute docRept. |
| rPer | Contains the period of look through values, the attribute "docRept". |
| mTime, mTimeU, mLev, mCat, mVal | Defined inside tags with the attribute "docAMess" when parsing messages of the message archive:
|
| Special tags | |
| Special attributes of the standard tags | |
| body.docProcLang | Language of the executable procedures of the document, by defaults it is "JavaLikeCalc.JavaScript". |
| *.docRept="1s" | Tag with the specified attribute multiplies, during the formation, by shifting the time in the attribute "rTime" to the value specified in this attribute. |
| *.docAMess="1:PLC*" | Indicates the need for multiplication a tag with the attribute, by messages from the message archive for the specified time interval, according to the level "1" and the query template "PLC*", by the message category. In the query template, regular expressions can be specified "/{re}/". For this tag, in the process of multiplication, the following attributes are defined: mTime, mTimeU, mLev, mCat and mVal. |
| *.docAMessArchs="ArchMod0.Archivator0[;ArchModN.ArchivatorN]" | Appends the attribute "*.docAMess" by the list of archivers for reading messages. |
| *.docRevers="1" | Indicates the inverting of the multiplication order — the last one above. |
| *.docAppend="1" | Indication of the need to add the result of the procedure to the procedure tag. Otherwise, the result will replace the tag content. |
| body.docTime | Time of formation of the document. Used to set the attribute lTime in the time of the next formation of the document. It is not set by the user! |
| table.export="1" | Enable the ability to export the contents of the specified table to a CSV-file or other spreadsheet formats. |
3.9.8 Container (Box)
The container primitive is used to build composite widgets and/or the pages of the user interface.
Table. List of additional properties/attributes of the primitive "Container (Box)"
| Identifier | Name | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pgOpenSrc | Page: source of the opening | 3 | Full address of the page, included inside of the container. |
| pgGrp | Page: group | 4 | Group of the container of the pages. |
| backColor | Background: color | 20 | Background color. Color name in the view "{color}[-{alpha}]", where:
Examples:
|
| backImg | Background: image | 21 | Background image. The image name in the view "[{src}:]{name}", where:
Examples:
|
| bordWidth | Border: width | 22 | Border width. |
| bordColor | Border: color | 23 | Border color (details in attribute 20). |
| bordStyle | Border: style | 24 | Border style: "None", "Dotted", "Dashed", "Solid", "Double", "Groove", "Ridge", "Inset", "Outset". |
3.10 Database using to store libraries of widgets and projects
Storing data widgets, widget libraries and projects is implemented in DB, accessible by OpenSCADA. The database is organized according to the data belonging to the library-project. That is, a separate library-project is stored in a separate group of database tables. The list of widget libraries is stored in the index table of libraries called "VCALibs" and the "Libs" structure, and the list of projects in the index table "VCAPrjs" and the structure "Projs". An instance of these tables is created in each database where the data of this module is stored. The tables belonging to the widget library and the project include the following:
- "{DB_TBL}" — table of widgets belonging to the library (structure "LibWigets"), or pages belonging to the project (structure "ProjPages");
- "{DB_TBL}_io" — table of working properties of widgets and nested widgets of the library (structure "LibWidgetIO") or properties of project pages (structure "ProjPageIO");
- "{DB_TBL}_uio" — table of user properties of widgets and nested widgets of the library (structure "LibWidgetUserIO") or user properties of project pages (structure "ProjPageUserIO");
- "{DB_TBL}_incl" — table of widgets, included in widgets-containers, of the library (structure "LibWidgetIncl") or the project (structure "ProjPageWIncl");
- "{DB_TBL}_mime" — table of library resources and its widgets (structure "LibWidgetMime"), or the project and its pages (structure "ProjMime");
- "{DB_TBL}_stl" — table of values of styled parameters of the project (structure "PrjStlIO");
- "{DB_TBL}_ses" — table of data for the project execution mode, that is, sessions (the structure of "PrjSesIO").
Projections (structures) of basic tables are as follows:
- Libs(ID, NAME, DSCR, DB_TBL, ICO) — libraries of the widgets ID.
- ID — identifier;
- NAME — name;
- DSCR — description;
- DB_TBL — root of the tables of DB with the widgets;
- ICO — encoded (Base64) image of the icon of the library.
- LibWigets(ID, ICO, PARENT, PROC, PROC_PER, ATTRS, TIMESTAMP) — widgets ID of the library.
- ID — identifier;
- ICO — encoded (Base64) image of the icon of the widget.
- PARENT — address of the basic widget, in the view /wlb_originals/wdg_Box;
- PROC — internal procedure and procedure language of the widget;
- PROC_PER — period of the computation of the widget procedure;
- ATTRS — list of attributes of the widget, modified by the user.
- TIMESTAMP — time-stamp of the last modification.
- LibWidgetIO(IDW, ID, IDC, IO_VAL, SELF_FLG, CFG_TMPL, CFG_VAL) — work attributes ID of the widget IDW of the child widget IDC.
- IDW — identifier of the widget;
- ID — identifier of the attribute;
- IDC — child widget identifier;
- IO_VAL — value of the attribute;
- SELF_FLG — internal flags of the attribute;
- CFG_TMPL — template of the configuration element based on this attribute;
- CFG_VAL — value of the configuration element (link, constant ...).
- LibWidgetUserIO(IDW, ID, IDC, NAME, IO_TP, IO_VAL, SELF_FLG, CFG_TMPL, CFG_VAL) — user attributes ID of the widget IDW of the child widget IDC.
- IDW — identifier of the widget;
- ID — identifier of the attribute;
- IDC — child widget identifier;
- NAME — name of the attribute;
- IO_TP — type and main flags of the attribute;
- IO_VAL — value of the attribute;
- SELF_FLG — internal flags of the attribute;
- CFG_TMPL — template of the configuration element based on this attribute;
- CFG_VAL — value of the configuration element (link, constant ...).
- LibWidgetIncl(IDW, ID, PARENT, ATTRS) — included into the container IDW widgets ID.
- IDW — identifier of the widget;
- ID — identifier of the included widget instance;
- PARENT — address of the basic widget, in the view /wlb_originals/wdg_Box;
- ATTRS — list of attributes of the widget, modified by the user.
- LibWidgetMime(ID, MIME, DATA) — audio, video, media and other resources of the widgets ID of the library.
- ID — identifier of the resource.
- MIME — Mime data type of the resource, in the format — "{mimeType};{Size}".
- DATA — resource data, encoded with Base64.
- Projs(ID, NAME, DSCR, DB_TBL, ICO, USER, GRP, PERMIT, PER, FLGS, STYLE) — projects ID of the visualization interface.
- ID — identifier of the project;
- NAME — name of the project;
- DSCR — description of the project;
- DB_TBL — root of the tables of DB with the pages;
- ICO — encoded (Base64) image of the icon of the project;
- USER — owner of the project;
- GRP — users group of the project;
- PERMIT — rights of access to the project;
- PER — period of the project computation;
- FLGS — flags of the project;
- STYLE — typical style of the project.
- ProjPages(OWNER, ID, ICO, PARENT, PROC, PROC_PER, FLGS, ATTRS, TIMESTAMP) — pages ID which are hold in the project-page OWNER.
- OWNER — project-page — owner of the page, in the format — "/AGLKS/so/1/gcadr";
- ID — identifier of the page;
- ICO — encoded (Base64) image of the icon of the page;
- PARENT — address of the basic widget of the page, in the format /wlb_originals/wdg_Box;
- PROC — internal procedure and procedure language of the page;
- PROC_PER — period of the computation of the widget procedure;
- FLGS — flags of the page;
- ATTRS — list of attributes of the widget, modified by the user;
- TIMESTAMP — time-stamp of the last modification.
- ProjPageIO(IDW, ID, IDC, IO_VAL, SELF_FLG, CFG_TMPL, CFG_VAL) — working attributes of the pages. The structure actually corresponds to the table "LibWidgetIO".
- ProjPageUserIO(IDW, ID, IDC, NAME, IO_TP, IO_VAL, SELF_FLG, CFG_TMPL, CFG_VAL) — user attributes of the pages. The structure actually corresponds to the table "LibWidgetUserIO".
- ProjPageWIncl(IDW, ID, PARENT, ATTRS) — widgets, included on the page. The structure actually corresponds to the table "LibWidgetIncl".
- ProjMime(ID, MIME, DATA) — audio, video, media and other resources of the project pages. The structure actually corresponds to the table "LibWidgetMime".
- PrjStl(ID, V_0, V_1, V_2, V_3, V_4, V_5, V_6, V_7, V_8, V_9) — value of the style's field ID of the project.
- ID — identifier of the style's field;
- V_{N} — value of the style's field for the style N.
- ProjSess(IDW, ID, IO_VAL) — project table IDW for data storage of the sessions, performing the project.
- IDW — full path of the project element;
- ID — attribute of the element;
- IO_VAL — value of the element.
3.11 API of the user programming and service interfaces of OpenSCADA
3.11.1 API of the user programming
API of the user programming of the visualization engine are represented directly by the OpenSCADA objects, which form the user interface, that is by the "Session" and "Widgets-pages". For the user, these objects provide a set of control functions:
Object "Session" ( this.ownerSess() )
- string user( ) — current session user.
- int alrmQuietance( int quit_tmpl, string wpath = "", bool ret = false ) — quiets of the violations wpath with the template quit_tmpl. If wpath is empty string then the global quietance makes. Into the string wpath, by symbol ';', can be enumerated addresses of several widgets. When set the ret, the quietance return is performed.
- int reqTm( ) — last request time.
- string reqUser( ) — last request user.
- string reqLang( ) — last request language.
- int userActTm( ) — last user action time.
Object "Widget" (this)
- TCntrNodeObj ownerSess( ) — session object for the current widget.
- TCntrNodeObj ownerPage( ) — parent page object for the current widget.
- TCntrNodeObj ownerWdg( bool base = false ) — parent widget object for the current widget. If set base then returns the parent page objects also.
- TCntrNodeObj wdgAdd( string wid, string wname, string parent ) — adds the new widget wid with the name wname and based on the library widget parent.
//Adds the new widget, based at the text primitive
nw = this.wdgAdd("nw", "New widget", "/wlb_originals/wdg_Text");
nw.attrSet("geomX", 50).attrSet("geomY", 50);
- bool wdgDel( string wid ) — deletes the widget wid.
- TCntrNodeObj wdgAt( string wid, bool byPath = false ) — attaches to child or global widget, by the path byPath. In the case of global connection, you can use absolute or relative path to the widget. For starting point of the absolute address acts the root object of the module "VCAEngine", which means the first element of the absolute address is session identifier, which is ignored. The relative address takes the countdown from the current widget. Special element of the relative address is an element of parent node "..".
- bool attrPresent( string attr ) — checks to presence fact of the attribute attr of the widget.
- ElTp attr( string attr, bool fromSess = false ) — value of the attribute attr of the widget or from the session fromSess. For missing attributes will be return empty string.
- TCntrNodeObj attrSet( string attr, ElTp vl, bool toSess = false ) — sets the value vl to the attribute attr of the widget or to the session, by toSess. The object is returned for the function concatenation.
- string link( string attr, bool prm = false ) — link for the widget attribute attr. At set prm requests the link for the attributes block (parameter), represented by the attribute.
- string linkSet( string attr, string vl, bool prm = false ) — sets the link for the widget attribute attr. At set prm, sets the link for the attributes block (parameter), represented by the attribute.
//Sets the link to the parameter for the eight trend
this.linkSet("el8.name", "prm:/LogicLev/experiment/Pi", true);
- string mime( string addr, string type = "" ) — "mime" object by the address addr (the direct link to the resource or the widget attribute contained the link) with the type in type, from the session table or the source. It is designed for the "mime" objects edition and that substitution to this session's context, for example, images SVG.
- int mimeSet( string addr, string data, string type = "" ) — sets the "mime" object to data with type by the address addr.
- int messDebug( string mess ); int messInfo( string mess ); int messNote( string mess ); int messWarning( string mess ); int messErr( string mess ); int messCrit( string mess ); int messAlert( string mess ); int messEmerg( string mess ); — formats of the program message mess with the category — the widget path.
Object "Widget" of the primitive "Document" (this)
- string getArhDoc( int nDoc) — text of the archive document to "nDoc" depth (0-{aSize-1}).
Deprecated, but supported, the API is represented by a group of functions directly in the module of the VCA engine. Calling these functions from the widget procedure can be done directly by the identifier, since their namespace is defined in the context of the widget procedures.
Widgets list (WdgList)
Description: Returns a list of the widgets, into the widgets container, or the child list. If set pg then returns the pages list for projects and sessions.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| list | List | String | Return | |
| addr | Address | String | Input | |
| pg | Pages | Boolean | Input | 0 |
Node presence (NodePresent)
Description: Checking for the node presence, including widgets, attributes and other.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rez | Result | Boolean | Return | |
| addr | Address | String | Input |
Attributes list (AttrList)
Description: Returns an attributes list of the widget. If set noUser then returns only not user attributes.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| list | List | String | Return | |
| addr | Address | String | Input | |
| noUser | Not user | Boolean | Input | 1 |
Get the attribute (AttrGet)
Description: Getting value of the widget attribute. The request can be done as by indicating the full address of the attribute in addr, and by: indicating separately the address of the widget in addr and the the attribute identifier in the attr.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | Value | String | Return | |
| addr | Address | String | Input | |
| attr | Attribute | Boolean | Input |
Set the attribute (AttrSet)
Description: Setting value of the widget attribute. Setting can be done as by indicating the full address of the attribute in addr, and by: indicating separately the address of the widget in addr and the the attribute identifier in the attr.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| addr | Address | String | Input | |
| val | Value | String | Input | |
| attr | Attribute | Boolean | Input |
Session user (SesUser)
Description: Returns the session user by the session widget path.
Parameters:
| Identifier | Name | Type | Mode | By default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| user | User | String | Return | |
| addr | Address | String | Input |
3.11.2 Service interfaces of OpenSCADA
Service interfaces are the interfaces for access to OpenSCADA through the OpenSCADA control interface. This mechanism is the basis of all mechanisms of exchange within OpenSCADA, implemented through weak links and the standard exchange protocol of OpenSCADA .
3.11.2.1 Access to the attributes values of the visualization elements (widgets)
In order to provide unitized, grouping and relatively fast access to the attributes values of the visual elements, the service function of the visual element "/serv/attr" and get-set commands of values of the attributes are provided:
- get: <get path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattr"/>;
- set: <set path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattr"/>.
Table. Attributes of the commands for get-set of the attributes of the visual elements.
| Identifier | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Requesting command of the visual attributes of the widget: <get path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattr"/> | ||
| tm | Time-counter of the changes | Time-counter of the changes set up for the query of the only changed attributes. |
| <el id="{attr}" p="{a_id}">{val}</el> | Formation of the child elements with the results of the attributes | In the child element are specified: string identifier attr, index a_id and value val of the attribute. |
| Setting command of the visual attributes of the widget: <set path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattr"/> | ||
| <el id="{attr}">{val}</el> | Setting of the attributes | In the child elements are specified: the string identifier attr and value val of the attribute. |
| Activation-creation command of the specific attribute for the visualizer: <activate path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattr/{attrId}" aNm="{Name}" aTp="{Type} aFlg="{Flags}"/> | ||
| attrId | Attribute identifier | |
| aNm | Attribute name | |
| aTp | Attribute type | |
| aFlg | Attribute flags | |
3.11.2.2 Group access to the values of the attributes of the visualization elements (widgets)
In order to optimize network traffic by eliminating the small queries and use one large, the group query of the attributes' values of the visual elements is made. Grouping of this query involves a request of attributes of the entire branch of the widget, including the included elements. For this request the service command "/serv/attrBr" provides. Request of this service command is equivalent to the service command "/serv/attr" and looks as follows: <get path="/UI/VCAEngine/{wdg_addr}/%2fserv%2fattrBr"/>
- tm — time-counter of the changes. time-counter of the changes set up for the query of the only changed attributes.
Result:
- <el id="{attr}" p="{a_id}">{val}</el> — elements with the results of the attributes. In the element are specified: string identifier attr, index a_id and value val of the attribute.
- <w id="{wid}" lnkPath="{lnk_path}">{childs+attrs}</w> — elements with the child widgets and their attributes. The element specifies: identifier of the child widget wid and the widget path, to which this widget refers if it is a link lnk_path.
3.11.2.3 Access to the session pages
In order to unify and optimize the access to the pages, the service function of the session "/serv/pg" and commands are provided:
- query of the list of opened pages: <openlist path="/UI/VCAEngine/ses_{Session}/%2fserv%2fpg"/>;
- open the page: <open path="/UI/VCAEngine/ses_{Session}/%2fserv%2fpg"/>;
- close the page: <close path="/UI/VCAEngine/ses_{Session}/%2fserv%2fpg"/>.
The result of the query is child elements <el>{OpPage}</el>, which contain the full path of the open page. In addition to the list of open pages, the query returns the value of the current counter for calculating the session, in the attribute tm. If this attribute is set during the query, then for, each open page, it returns the list of changed, since the moment of the specified value of the counter, widgets of the open page.
3.11.2.4 Control for signaling (alarming)
To provide a mechanism for global control of the signaling of the session, the service function of the session "/serv/alarm" and commands are provided:
- query of the signals status: <get path="/UI/VCAEngine/ses_{Session}/%2fserv%2falarm"/>;
- quietance of the signals: <quietance path="/UI/VCAEngine/ses_{Session}/%2fserv%2falarm"/>.
Request for the signals status returns generalized state of the signals, as well as the resource of the notification if the "mode" attribute is "resource". The result of the notification resource request is usually a sound file for playback. At the same time, the tracking of the sequence of signaling and the quietance of individual notification resources is provided.
Request for the quietance performs the quietance of the widget, specified in the attribute wdg, in accordance with the template in the attribute tmpl.
3.11.2.5 Manipulation with the sessions of the projects
To provide a unitize mechanism for manipulation of the sessions, the module of the VCA engine (VCAEngine), for the visualizers of VCA, is provided the service function "/serv/sess" and the commands:
- query of the list of open sessions: <list path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/>;
- connection-creation of the new session: <connect path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/>;
- disconnection-deleting of the session: <disconnect path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/>.
Table. Attributes of commands of the mechanism of manipulation with sessions
| Identifier | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Command of requesting of a list of open sessions for the project: <list path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/> | ||
| prj | Indication of the project | Specifies the project for which to return the list of opened sessions. |
| <el>{Session}</el> | Control of the sessions' list | The child elements specify the sessions opened to the requested project. |
| Command of the connection-opening the session: <connect path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/> | ||
| sess | Installation and control of the session name | If the attribute is defined, then the connection to the current session is made, otherwise — the creation of a new session. In the case of opening a new session, the name of the new session is placed to the given attribute. |
| prj | Setting the name of the project | It is used to open a new session for the indicated project and when the attribute sess is not specified. |
| Command of the disconnection-closing of the session: <disconnect path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fsess"/> | ||
| sess | Setting the name of the session | Specifies the name of the session from which disconnection or closure is performed. Sessions that are not background and which are not connected to any visualizer are automatically closed. |
3.11.2.6 Group request for the tree of the widgets libraries
In order to optimize the performance of local and, especially, network interaction, the service function "/serv/wlbBr" and the command of the query of the tree of the widgets libraries: <get path="/UI/VCAEngine/%2fserv%2fwlbBr"/> are provided. The result of the query is a tree with the elements of the widgets libraries — tags wlb. The tags of widgets libraries are included: icon tag ico and the widgets library tags w. The widgets tags, in their turn, contain the icon tag and tags of the child widgets cw.
4 Configuring the module via the control interface of OpenSCADA
Through the control interface of OpenSCADA, components that use it, can be configured from any configurator OpenSCADA. This module provides an interface to access all the data object of the VCA. Main tab of the configuration page of the module provides access to widgets libraries and projects (Fig.4.1). The tab "Sessions" provides access to opened sessions of the projects (Fig.4.2).
In addition to the list of opened sessions, the tab in Figure 4.2 contains a table with a list of sessions that must be created and started up at the boot time of OpenSCADA. Creation of sessions through this tool can be useful for Web-based interface. In this case, when connecting, Web-user data is ready and ensures the continuity of the formation of archival documents.
Configuration of the container widgets in the face of libraries and widget projects is done through pages in Figure 4.3 (for project) and Figure 4.5 (for widgets library). The widgets library contains the widgets, and project — the pages. Both types contain a tab of configuration Mime-data used by widgets (Fig.4.6). The project page also contains the tab "Diagnostics" (Fig.4.4) for debugging and monitoring the execution of pages in sessions.
From this page you can set:
- State of the container, same: "Enabled", name of the database (containing the configuration), date and time of last modification, counter of the use.
- Identifier, name, description and icon of the container.
- Owner, group and access rights to the container.
- Period for computing of the sessions based on the given project.
- Signal of enabling as needed.
From this tab you can select time (or refresh to current) and size to obtain the diagnostic messages of the sessions of running this project.
From this page you can set:
- State of the container, same: "Enabled", name of the database (containing the configuration), date and time of last modification, counter of the use.
- Identifier, name, description and icon of the container.
Configuration of the project's session differs significantly from configuration of the project (Fig.4.7), but also contains pages of the project.
From this page you can set:
- State of the session, the same: "Enabled"; "Running"; user; owner; users group; access; source project; mode of execution in the background; execution time of the session; counter of client connections; last request time, user and language; last user action and remained time to it force closing.
- Period of the session calculation.
- Current style of the session.
- List of the opened pages.
Configuration pages of the visual elements, placed in different containers, may be very different, but this difference is the presence or absence of individual tabs. Main tab of the visual elements in fact is the same everywhere, differing in one configuration field and three into the session (Fig.4.8). The pages contains the tabs of the child pages and included widgets. The container widgets contains the tab of the included widgets. All visual elements contain attributes tab (Fig.4.9), except the logical containers of the projects. Elements, at the level of which it is possible to build the user procedure and to determine the links, contain the tabs "Process" (Fig.4.10) and "Links" (Fig.4.11).
From this page you can set:
- States of the element, the same: "Enabled", counter of the use, parent element and jump to it, date and time of the last modification.
- States of the runtime session's mode: "Opened", "Process" and spent time on execution of the subtree and item, into the debug mode.
- Identifier, type, root, path, name, description and icon of the element.
- Command — clear the widget changes.
- Command — lower down the widget changes to its parent.